Fundamental GC-MS
This learning path on fundamental GC-MS covers system setup, GC parameters (columns, carrier gases), and sample introduction techniques (split/splitless, headspace). It includes MS interfaces, ionization methods (EI, CI), and solvent delay optimization. Practical strategies focus on method development, contamination control, and ensuring accurate, high-sensitivity mass spectrometric analysis.
6 Modules 1 Quick Guide
7 Items
GC-MS Introduction
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is a hyphenated technique which combines the separating power of gas chromatography (GC) with the detection power of mass spectrometry (MS). This module will explore the instrument acquisition methods used and examine the type of data that can be produced from such systems.

Practical GC-MS Video Bootcamp
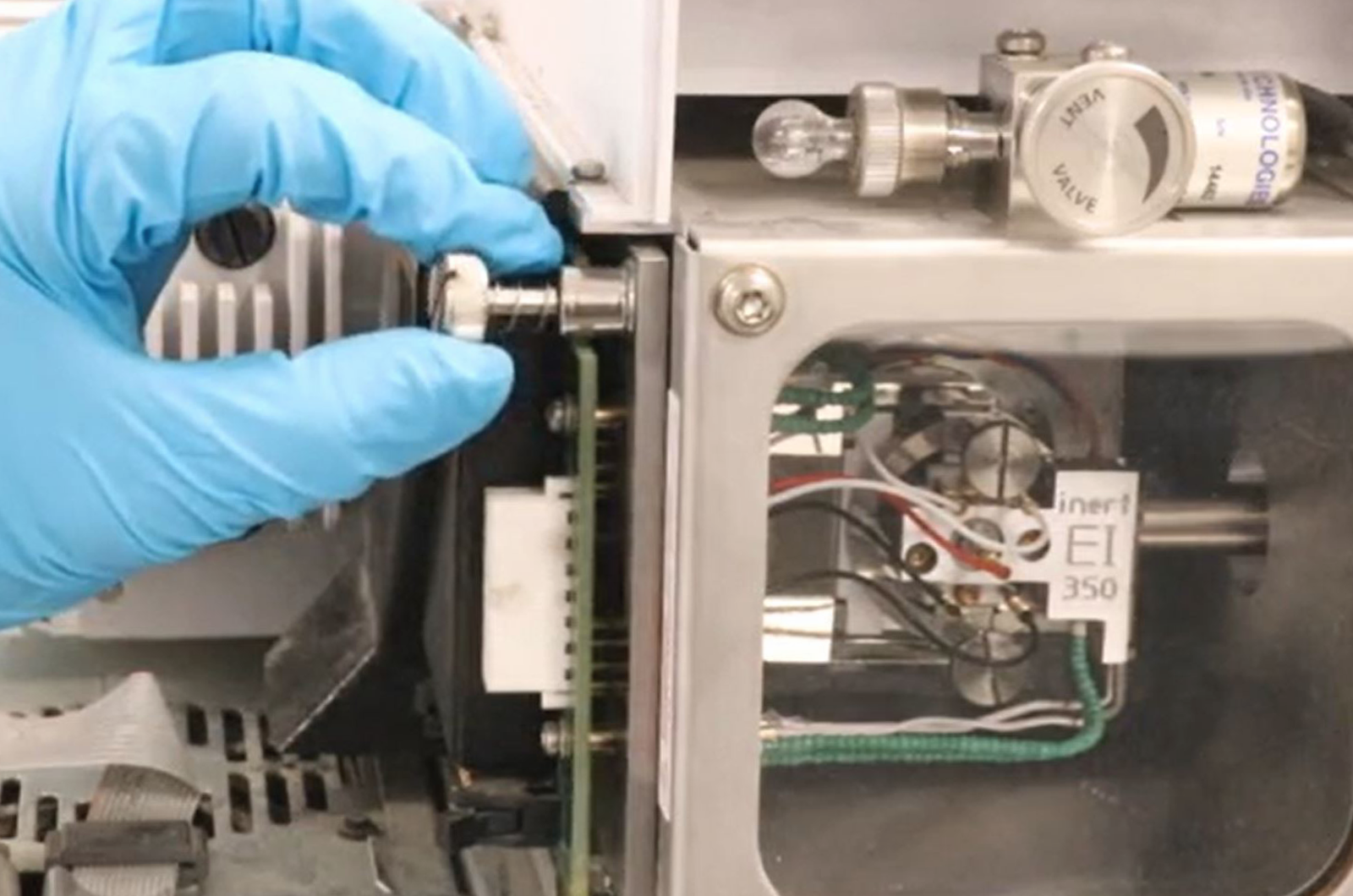
The definitive guide to setting up a GC-MS instrument. Working on a real GC-MS instrument we provide you with the fundamental knowledge on the science, working principles, and correct setup of this powerful piece of equipment. An in-depth tour of how to dismantle and clean the ion source will give you confidence to perform preventative maintenance on your instrument.
GC Considerations
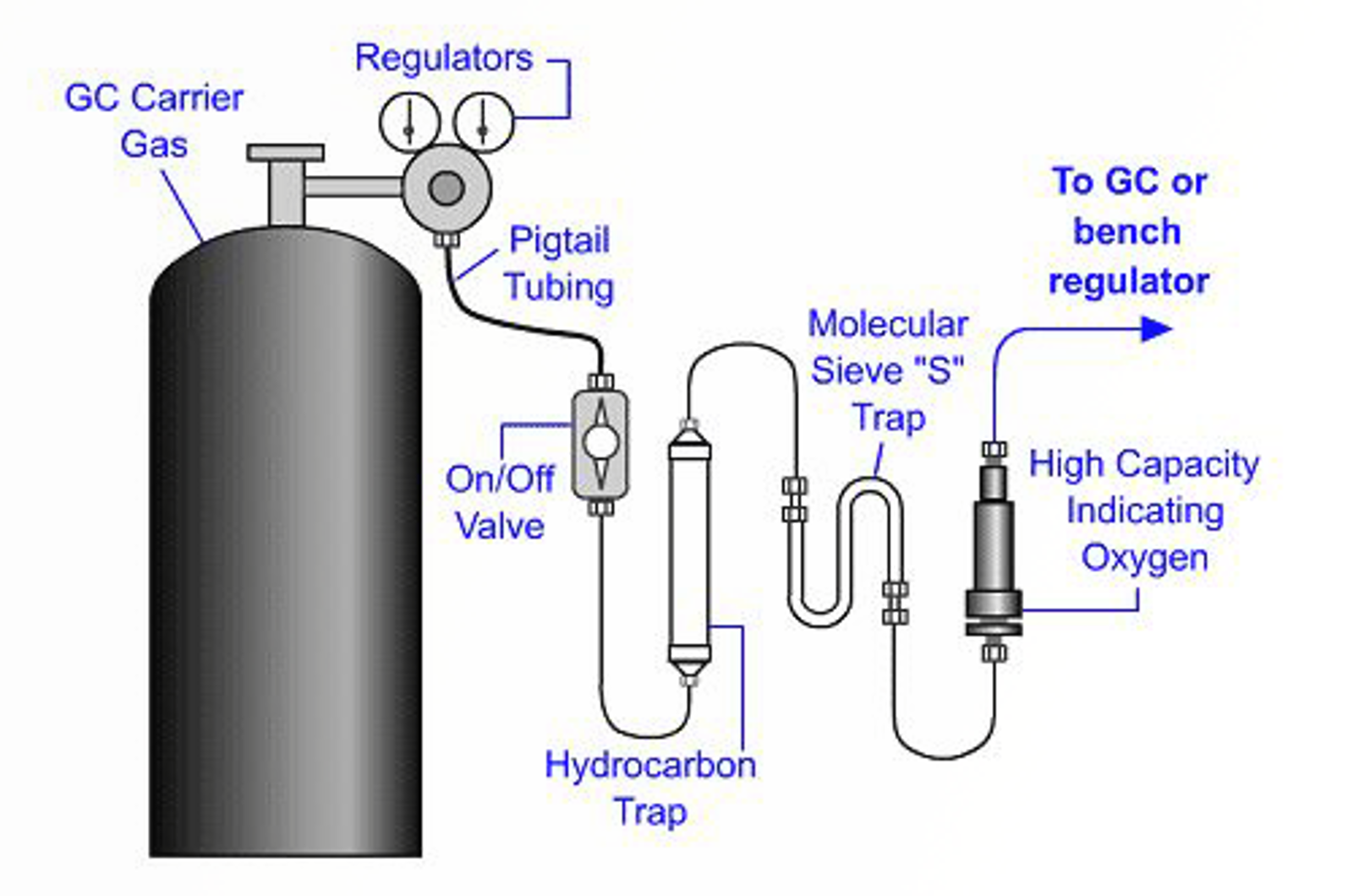
This module explores the main GC considerations when using MS detectors. The choice of column phase and dimensions are considered, as well as the effects of carrier gas flows on the MS vacuum system.
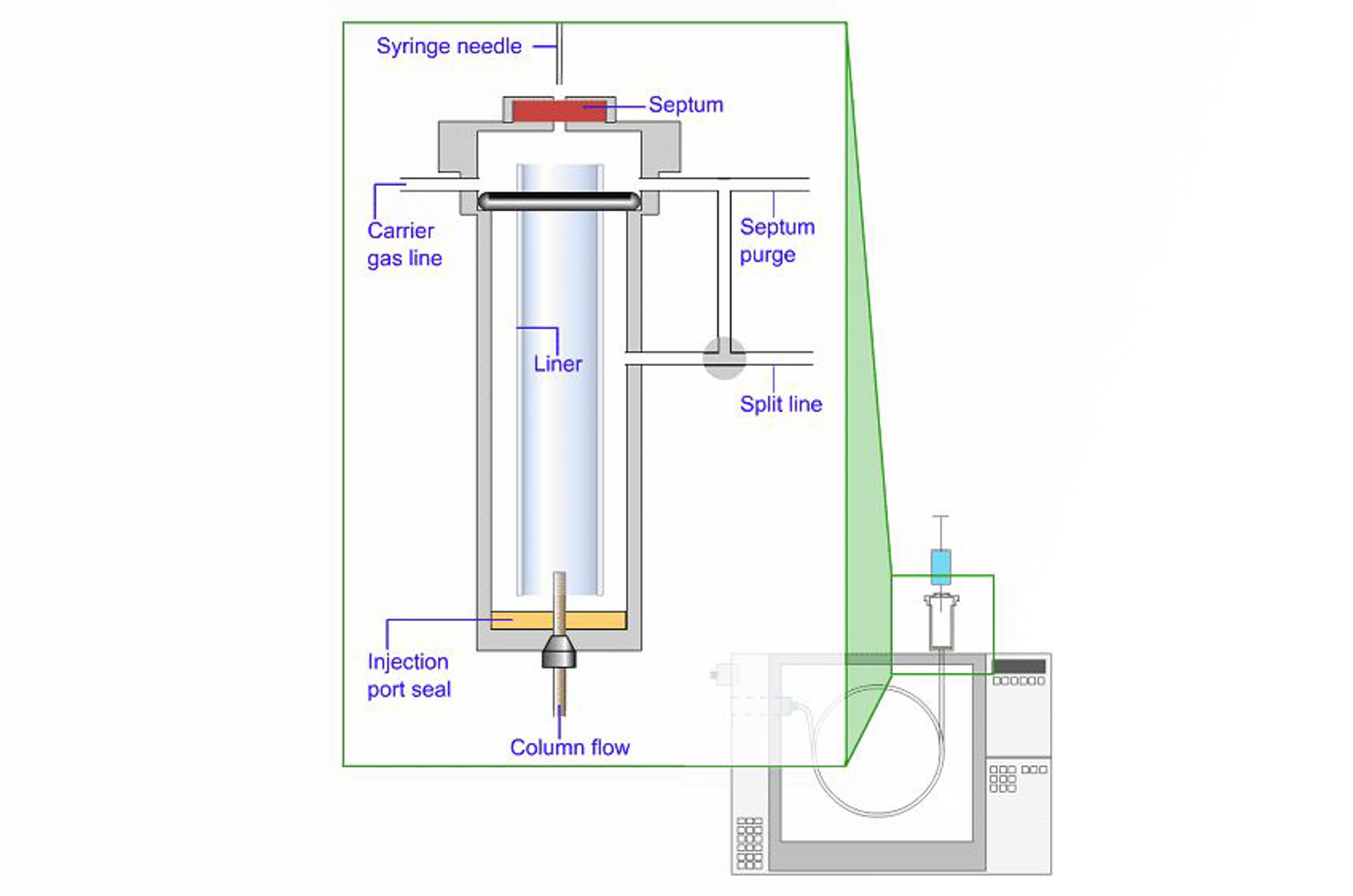
GC-MS Sample Introduction
Perhaps the most difficult step in any GC-MS analysis is the sample introduction. Solid or liquid samples need to be converted to the gas phase and then efficiently transported onto the GC column. The primary aim with all sampling techniques is to ensure a representative and homogeneous gaseous aliquot of the sample under investigation is delivered to the GC column. This module will explore the main GC considerations when using MS detectors.
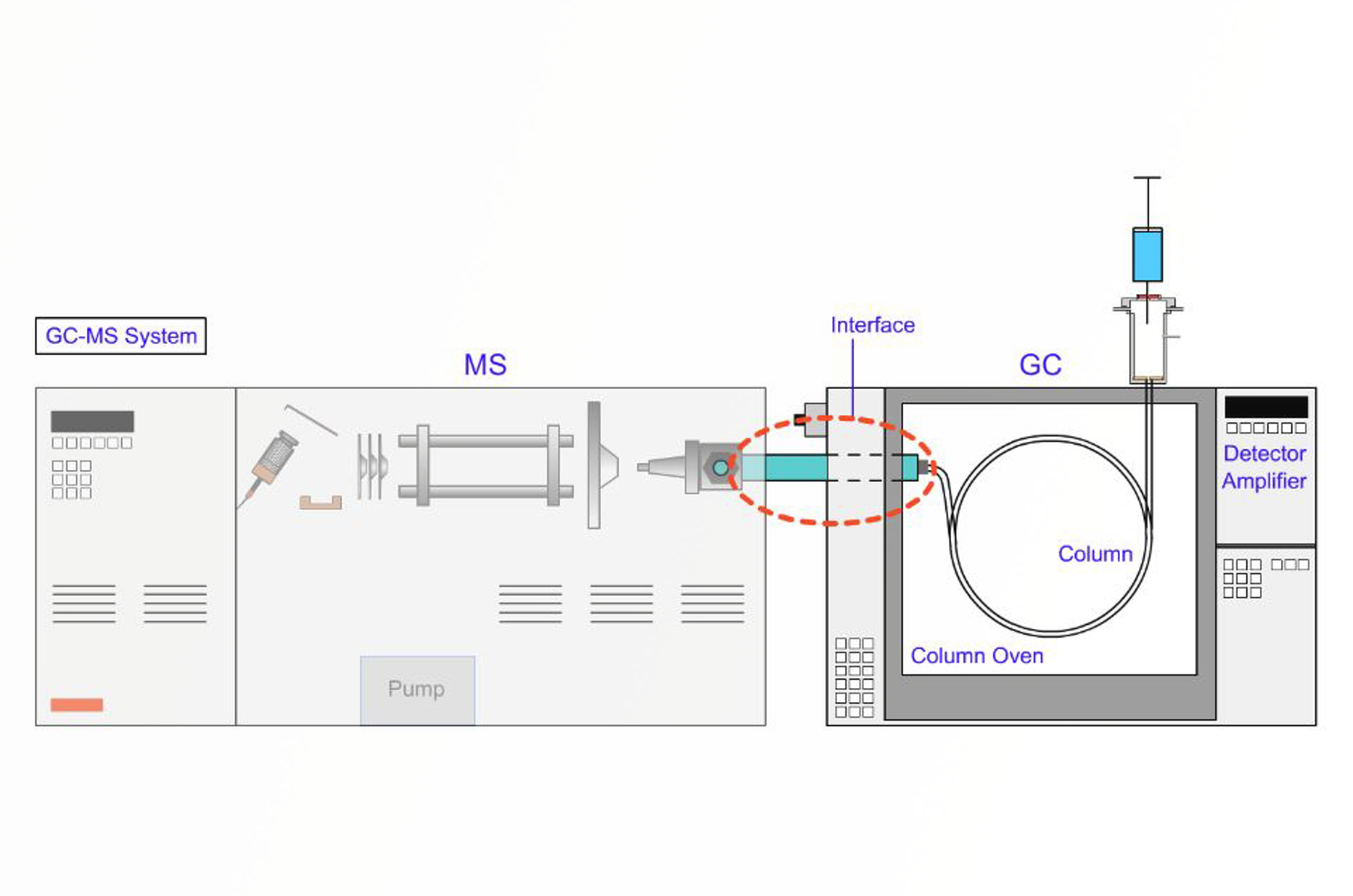
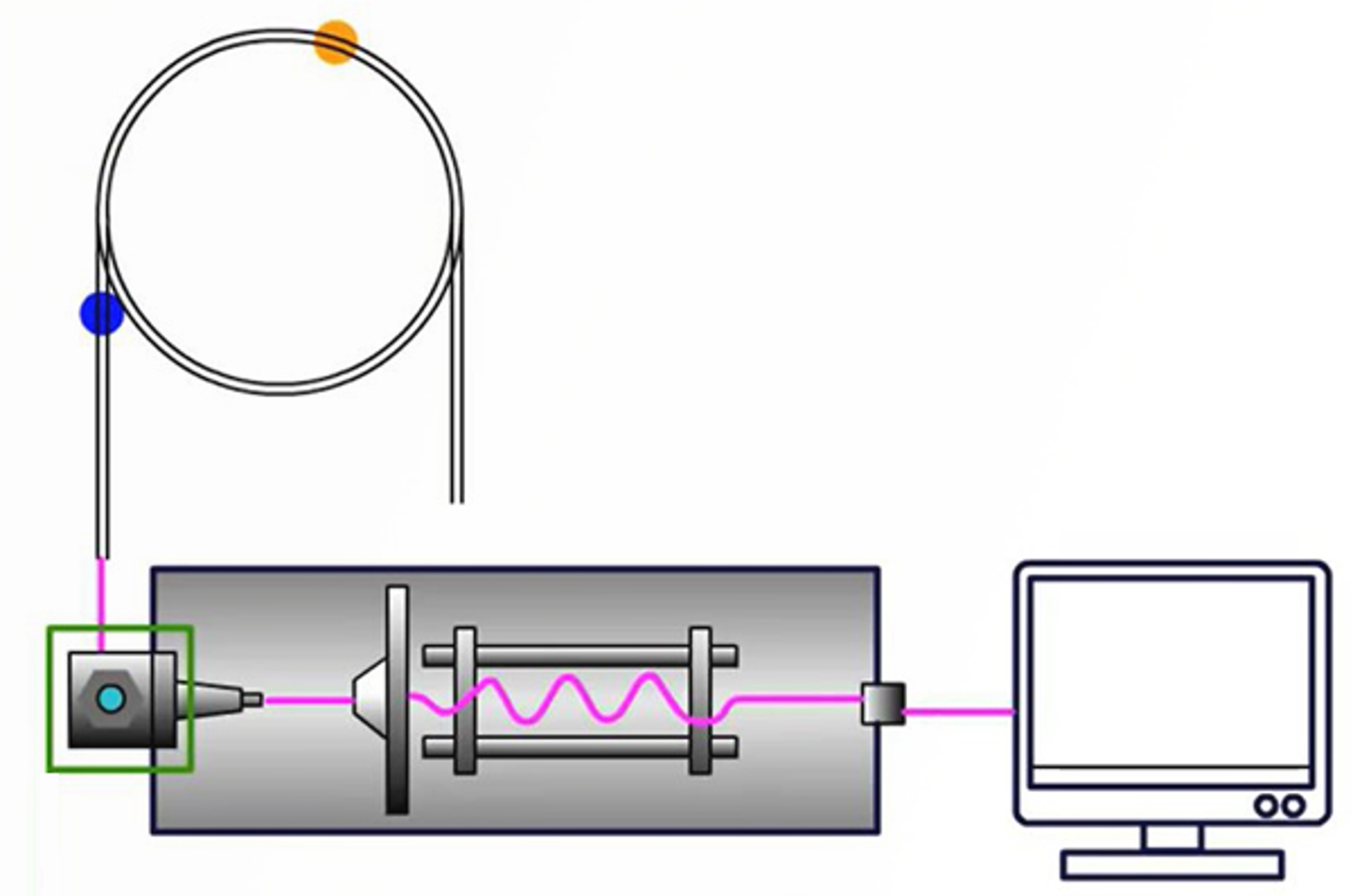
GC-MS Interfaces
After separation in the GC column, analyte species have to be transported to the mass spectrometer to be ionized, mass filtered, and detected. The column outlet needs to be connected to the ion source of the mass spectrometer and this module presents the correct interface types for use with different GC columns and MS instrument types.
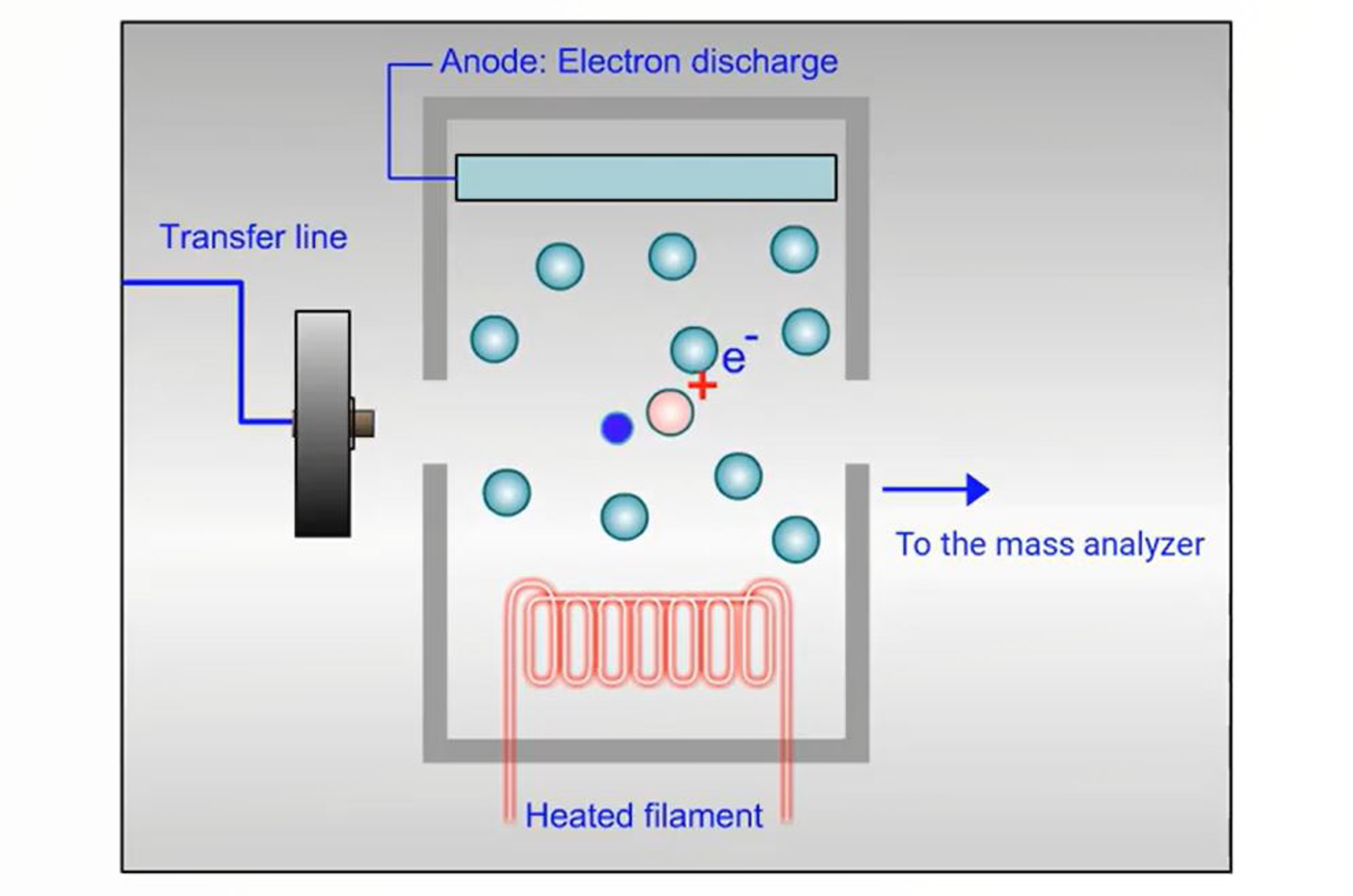
GC-MS Ionization
An introduction to the ionization processes which occur in GC-MS. Ionization is the process whereby electrons are either removed or added to atoms or molecules to produce ions.
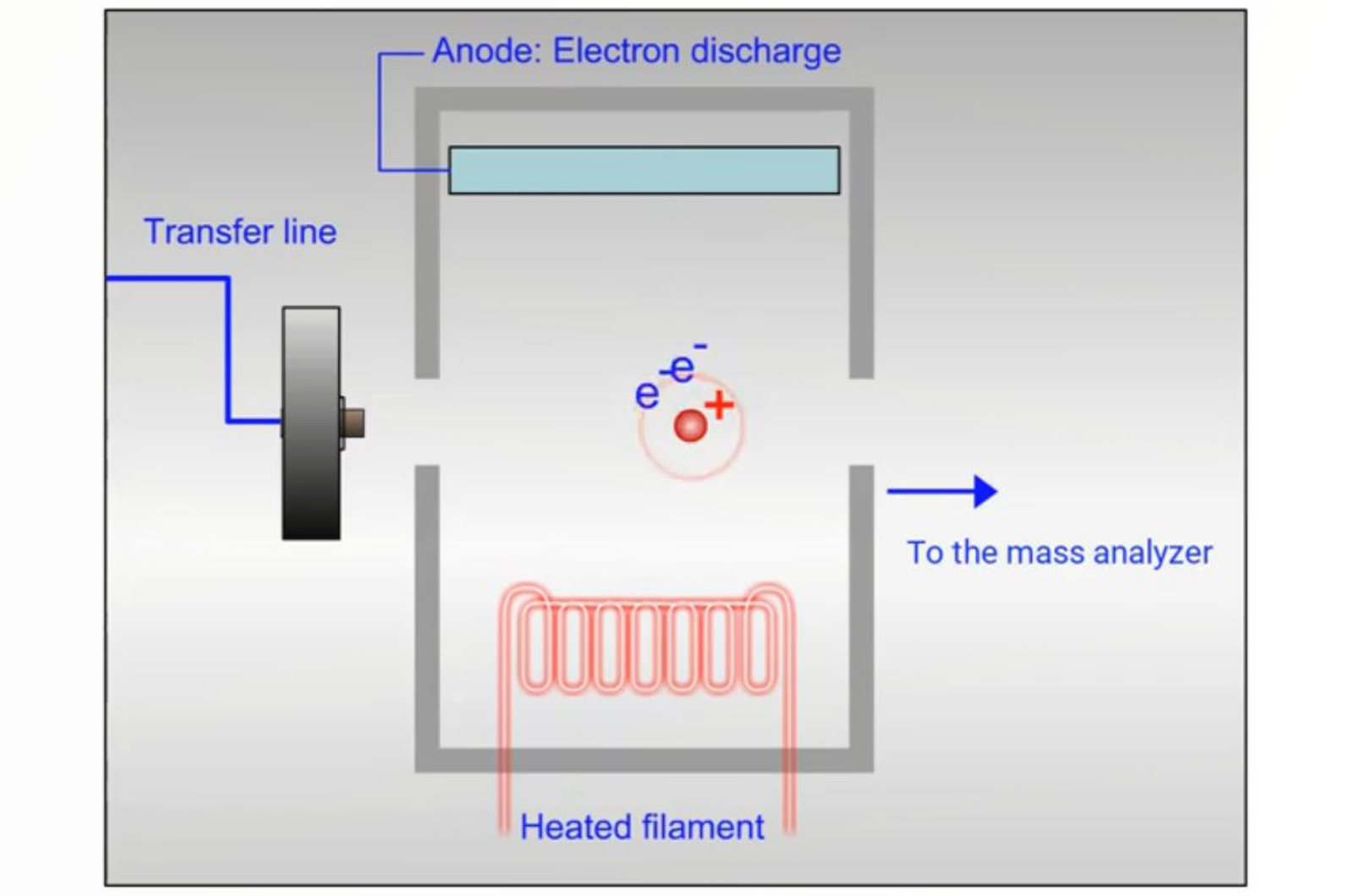
GC-MS Solvent Delay
Using GC-MS solvent delay helps to protect the filament in the ion source, meaning the instrument will perform how it should for longer. This quick guide will detail how to determine the solvent delay time for your method and outline the benefits of using this in every method.
