Technique
Explore the technique of HPLC. Master modes of chromatography, including reversed phase, normal phase, ion exchange, mixed-mode, HILIC, and size-exclusion HPLC. Learn instrument setup using our video bootcamp, covering mobile phase preparation, system setup and equilibration, and verification of system performance. Understand gradient HPLC for enhanced separation and optimized mobile phase control. Develop expertise in qualitative and quantitative HPLC, focusing on peak identification, retention time analysis, calibration, and internal standards. Designed for professionals in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food safety, and environmental analysis, CHROMacademy offers interactive learning with expert insights, animations, and quizzes.
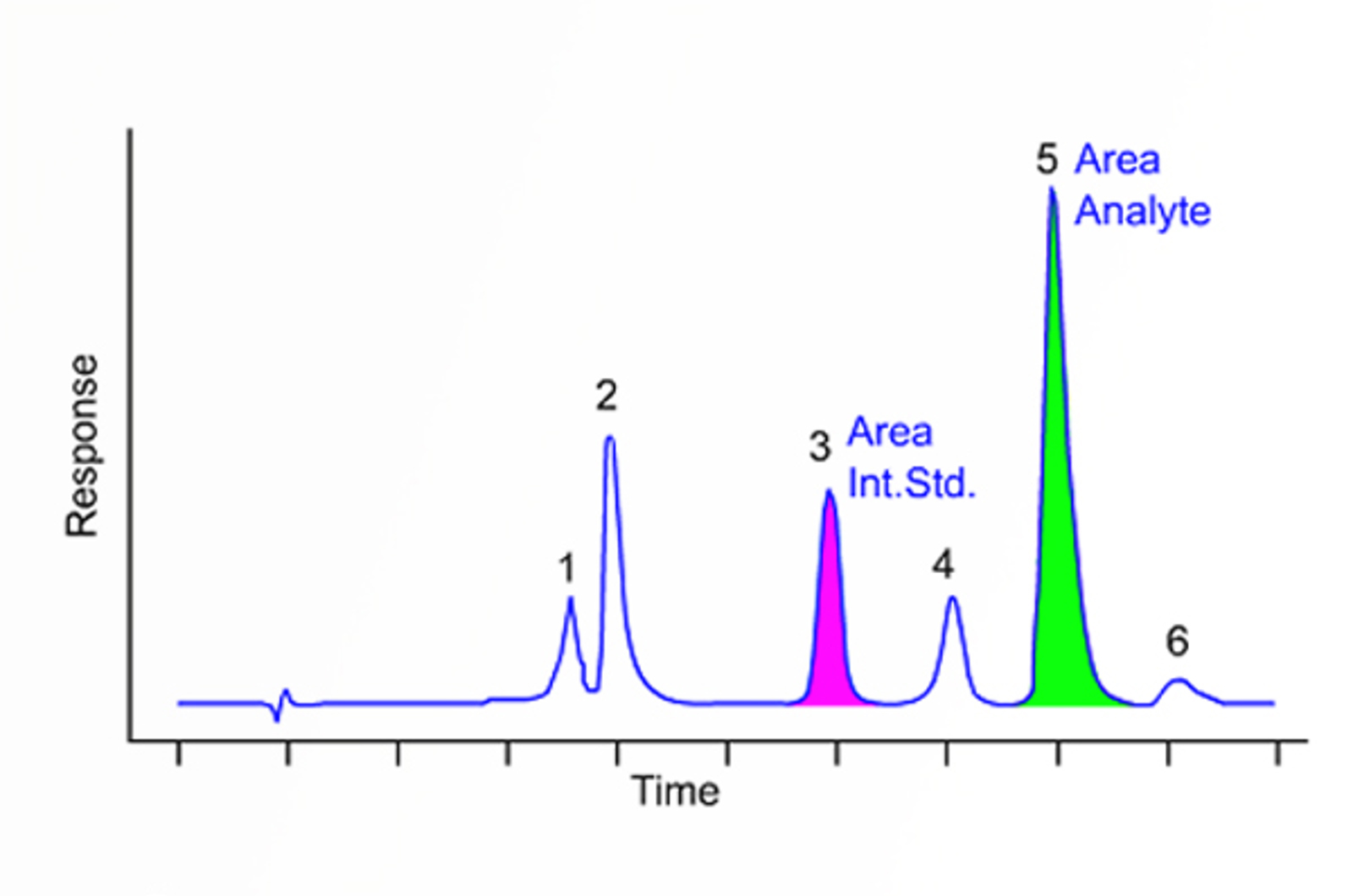
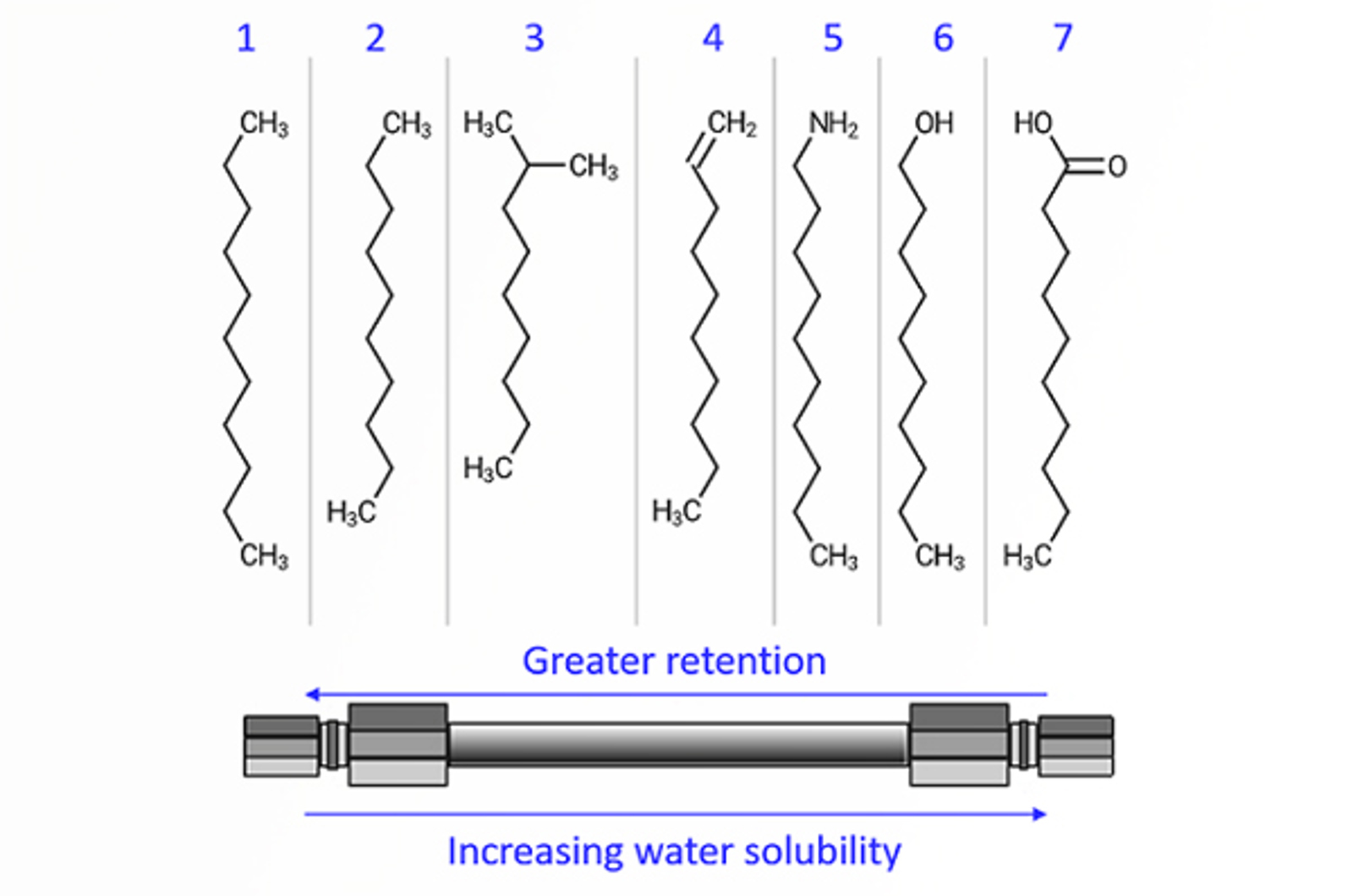
Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC
The aim of this module is to define quantitative HPLC and explain the information that can be derived from this type of HPLC analysis. We highlight the principles of peak identification and analyte characterization from a practical perspective.
Normal Phase Chromatography
The aim of this module is to give an overview of the mechanism of normal phase chromatography (NP-HPLC) and explain the basis of the retention mechanism. Retention order in NP-HPLC is explained, and the influence of mobile phase composition on retention demonstrated. We will illustrate how the mobile phase composition and constituents might be manipulated to optimize chromatographic separations in NP-HPLC. The principles which are used to select appropriate stationary phases and column geometry are also discussed.

Ion Pair Chromatography
The aim of this module is to explain the principles of ion pair chromatography and to demonstrate the circumstances under which this approach might be used. We investigate the common reagents used for ion pair chromatography and explain how to choose the appropriate reagents. We also demonstrate the effects of the important parameters associated with ion pair chromatography, concentrating on ion reagent choice and concentration.
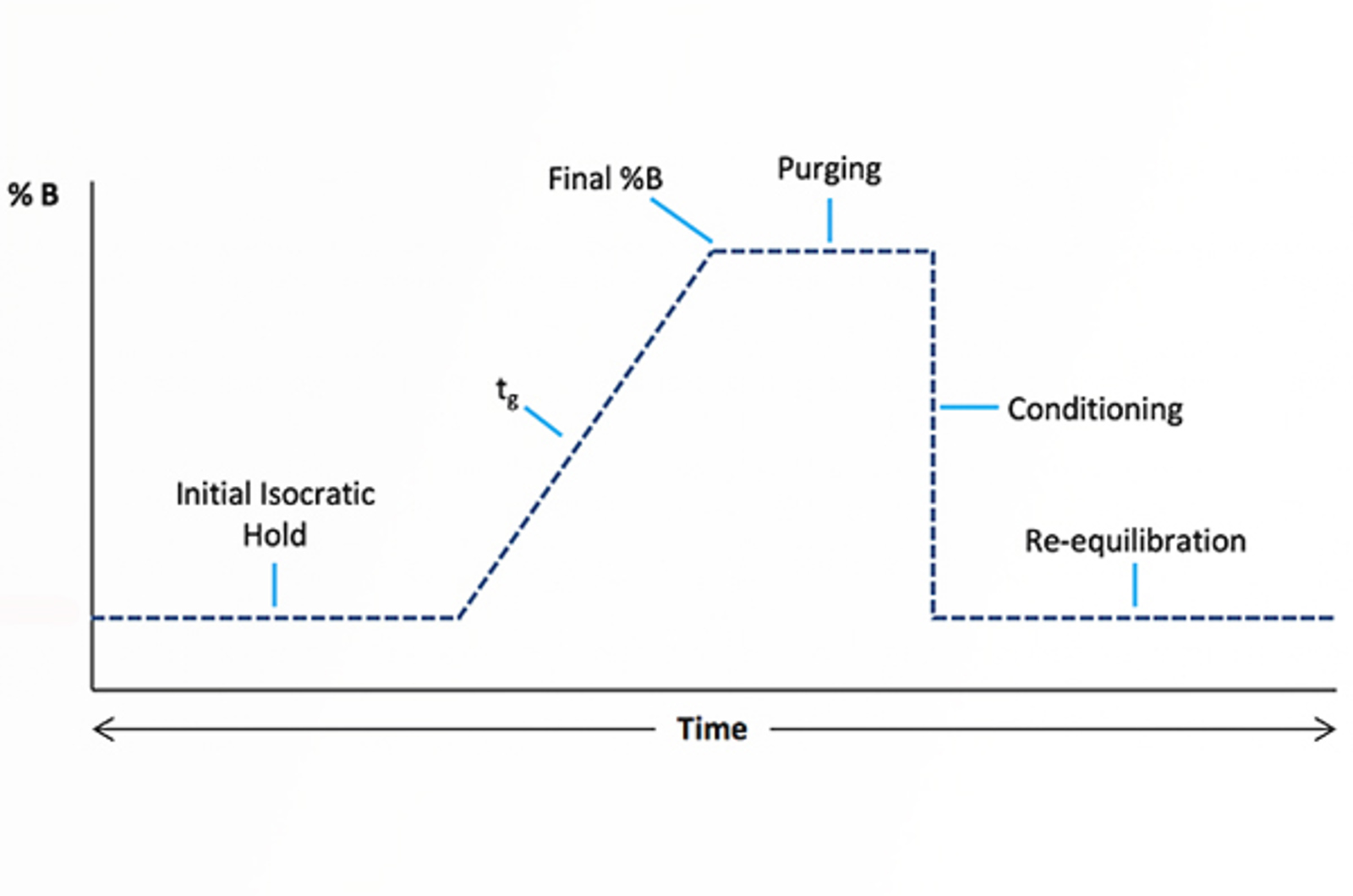
Gradient HPLC - 10 Things You Absolutely Need to Know
Everyone loves a top ten list, so here is our list of “Top Ten Things you Absolutely Need to Know About Gradient HPLC”. Whether you are a novice or seasoned gradient HPLC user, there is something in here for everyone.
Mixed-Mode Chromatography – The Answer to Everything?
In this session, our speakers consider the technique of mixed-mode chromatography and the application areas in which this technique can help chromatographers. The mechanisms of mixed-mode chromatography are discussed alongside the parameters which can be used to optimize selectivity and retention. A series of useful illustrative example are presented with strategies for column selection and screening to allow this technique to quickly become part of the analytical armory!
Introduction to Ion Chromatography
This webcast considers the underlying theory of the technique, column and eluent selection, and key separation variables; as well as the various techniques used for ion suppression and detection. We also consider various applications of ion chromatography together with recent advances in the technique including capillary ion chromatography, fast and ultra high pressure ion chromatography, and hyphenation of ion chromatography to mass spectrometric detectors.
Basics of Preparative HPLC
In this webcast, our speakers present an introductory guide to the theory, instrumentation, and applications of preparative HPLC. We consider all the relevant aspects of theory and practical implementation and will consider the requirements imposed at analytical scale when considering scale-up to prep.
Automated Inline Sample Preparation for Ion Chromatography - Doing More with Less
Industrial chemicals such as organic and mineral acids and organic solvents play a pivotal role in many processes. Their purity and the profile of impurities can be critical to the success or failure of a manufacturing facility. Here we will show automated inline sample preparation techniques for determining ionic impurities in a variety of important products. Brief examples of many types of treatment protocols will be described and the results shown.
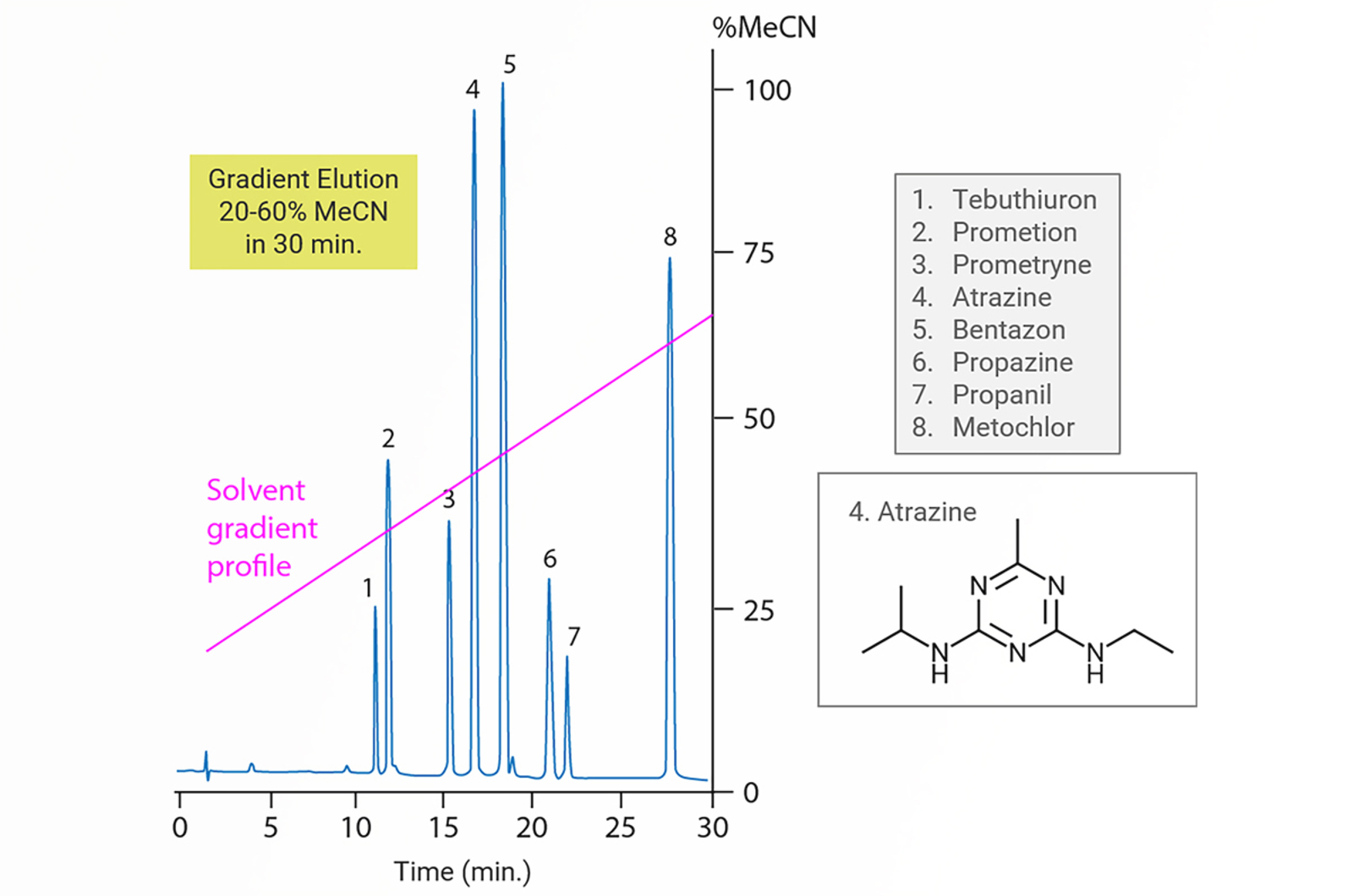
Gradient HPLC
The aim of this module is to explain the problems that can be encountered when using isocratic HPLC.
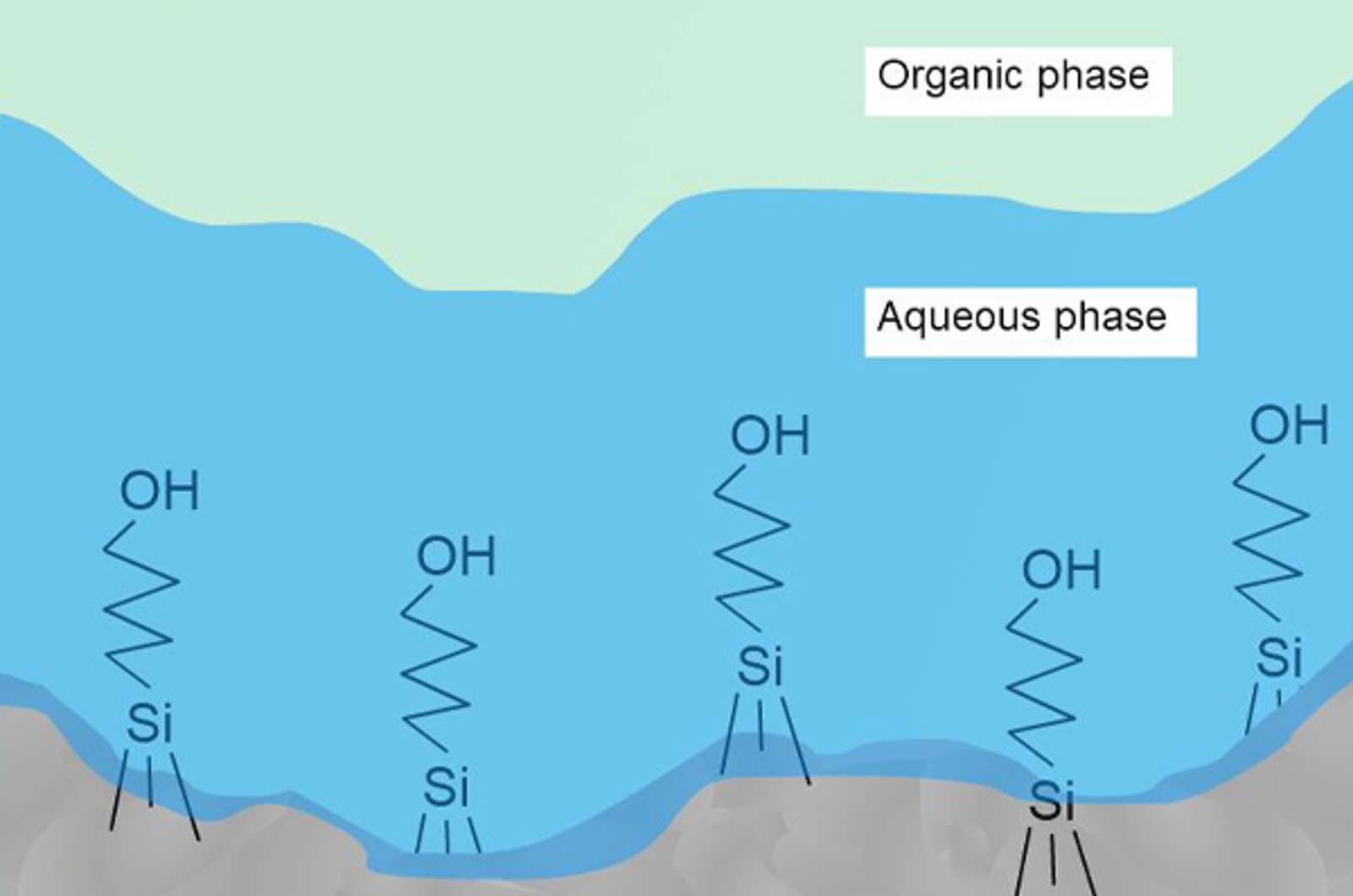
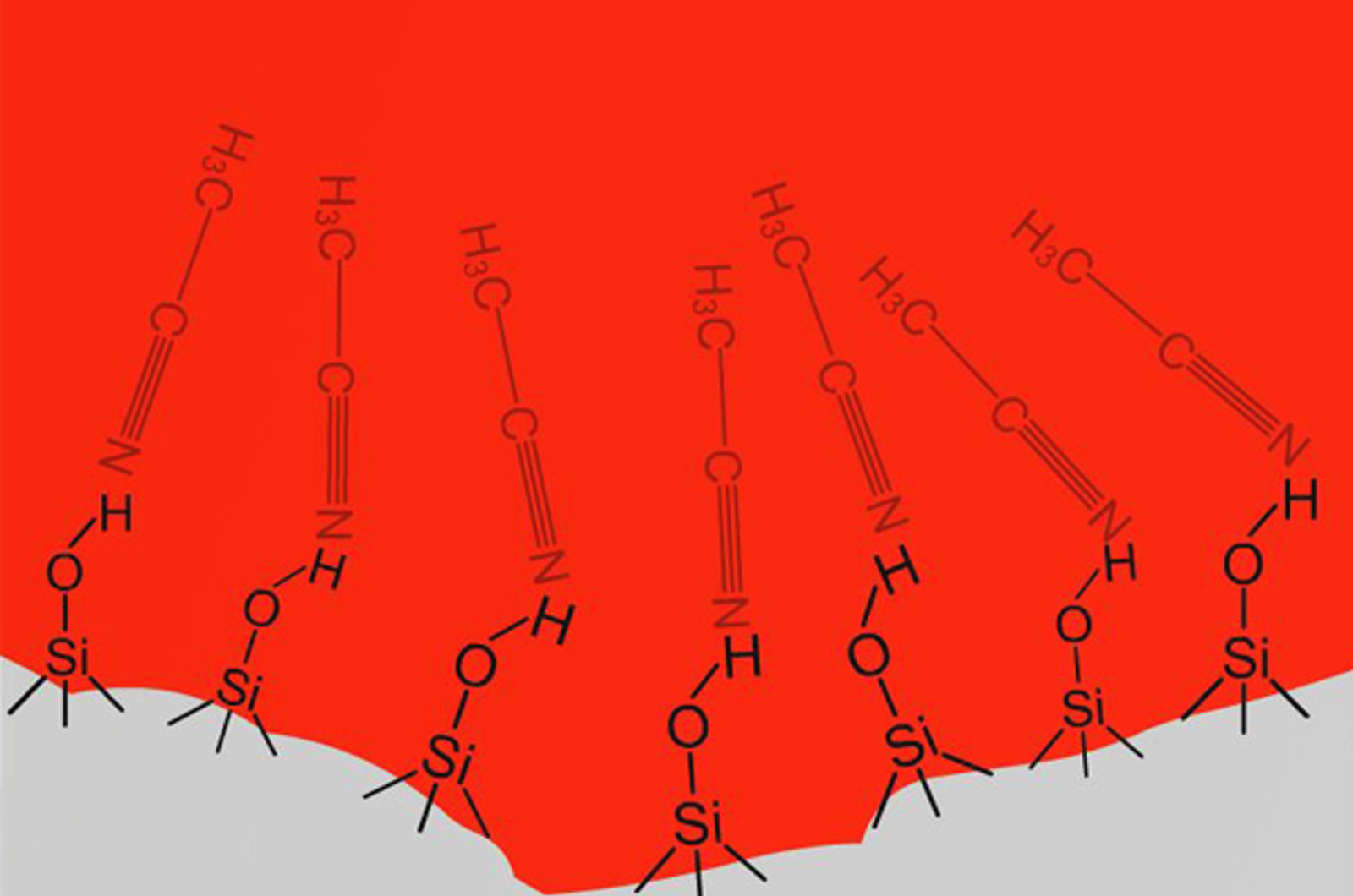
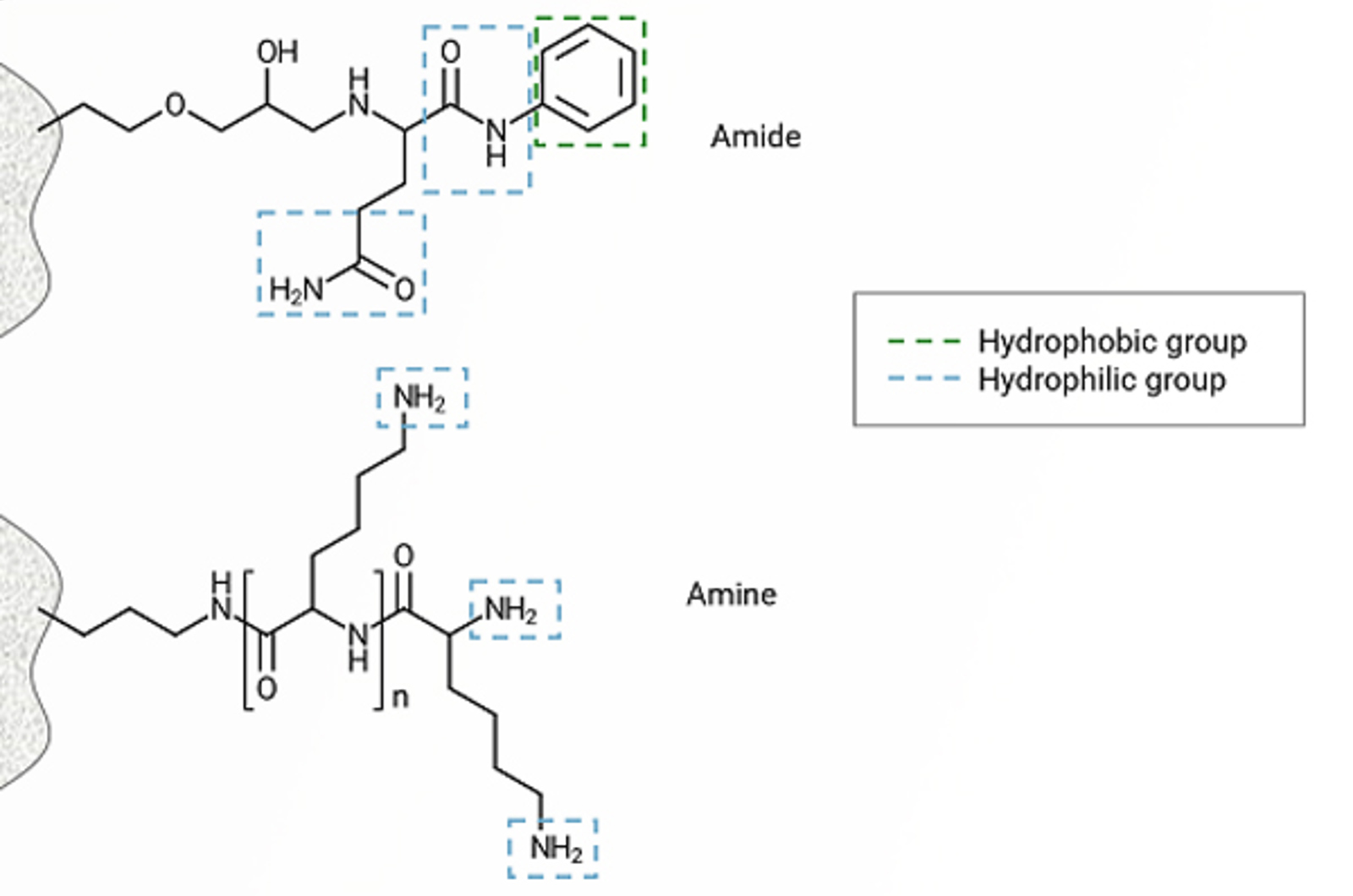
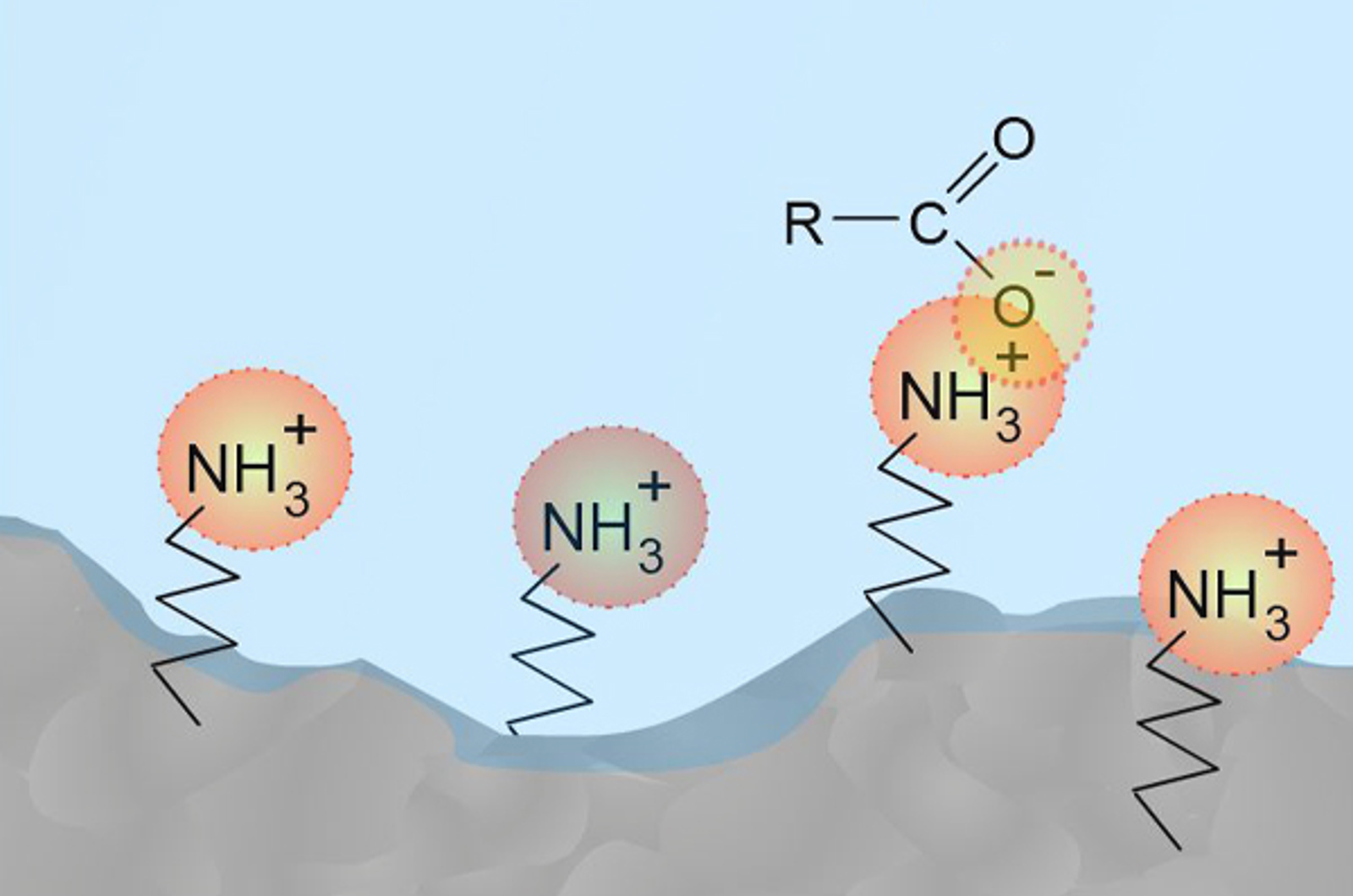
HILIC
The aim of this unit is to introduce hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) as a novel mode of chromatography. We will present both advantages and limitations of the HILIC separation mode. Electrostatic repulsion hydrophilic interaction chromatography (ERLIC) will also be discussed as a new HPLC option for hydrophilic analytes. The concepts of ion exchange chromatography and its separation potential for certain ionic samples will be explored.
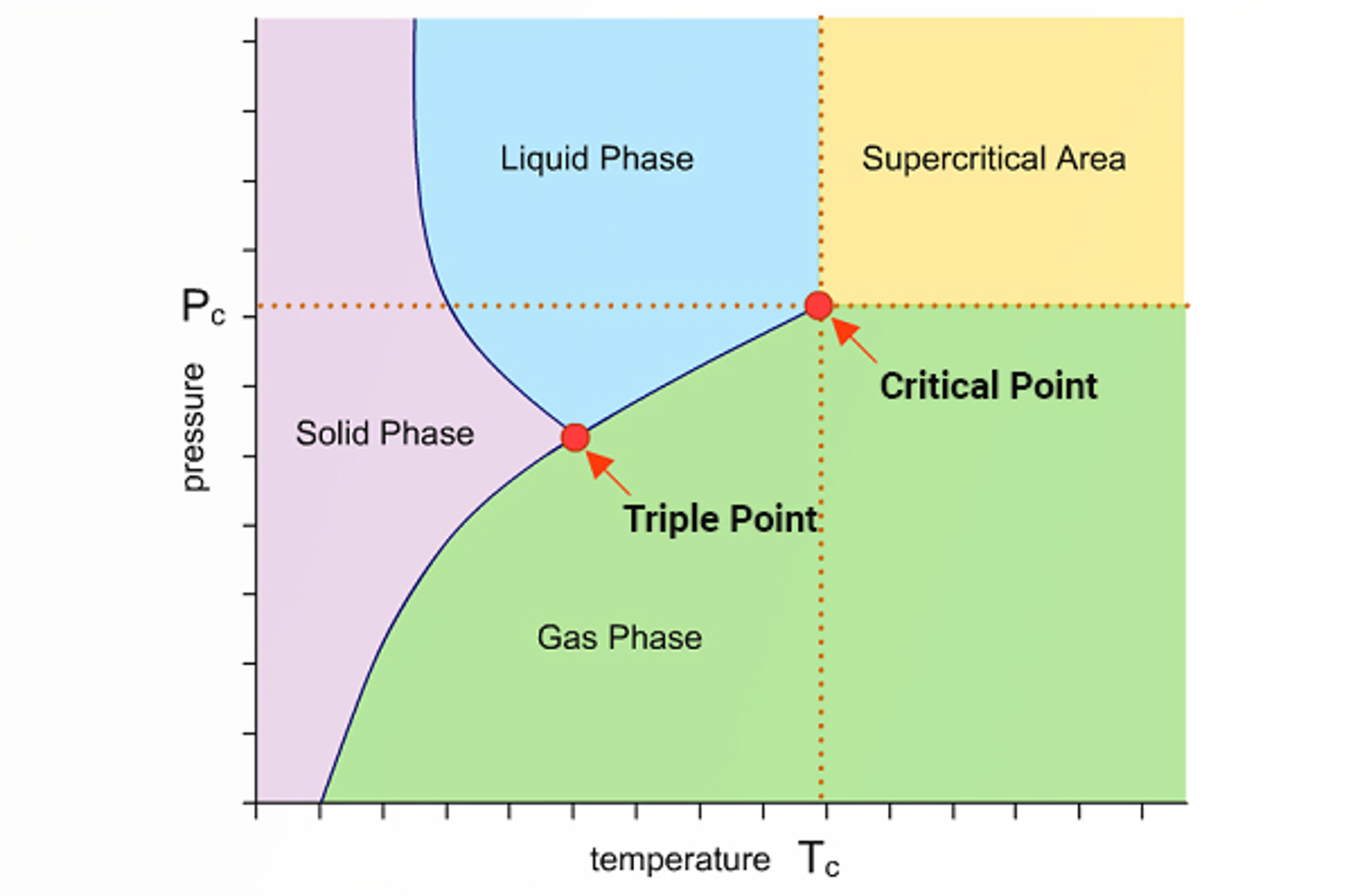
Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
The aim of this module is to introduce supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) as a powerful solution for chromatographic analysis. The basic aspects of SFC are explained and the fundamental hardware typically used with the technique discussed.
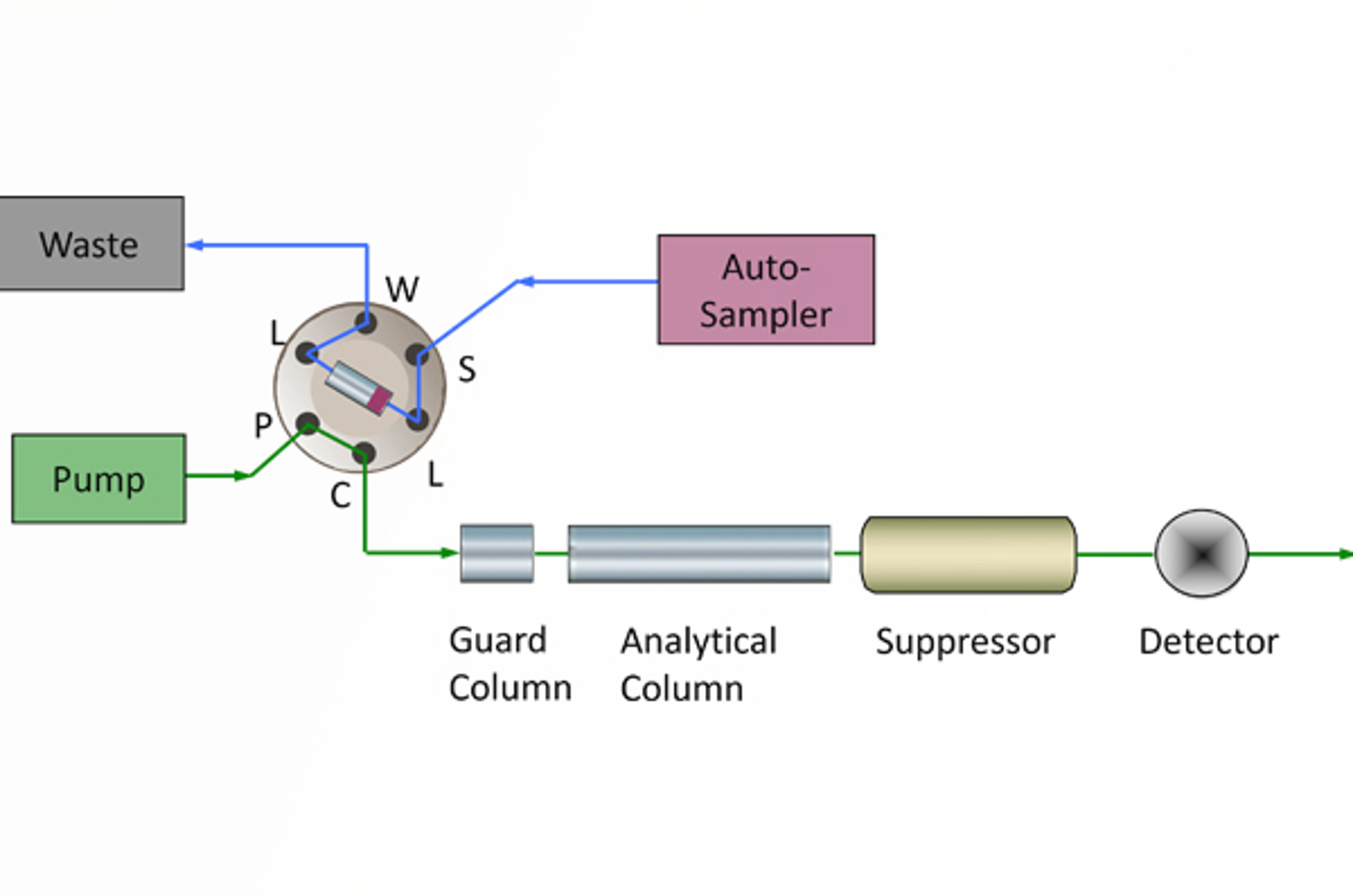
Ion Chromatography
The aim of this module is to introduce some of the working principles of ion chromatography and related techniques. The various approaches to analyzing ions in solution are highlighted. We will also explain the equipment/eluent modifiers necessary for ion chromatography.
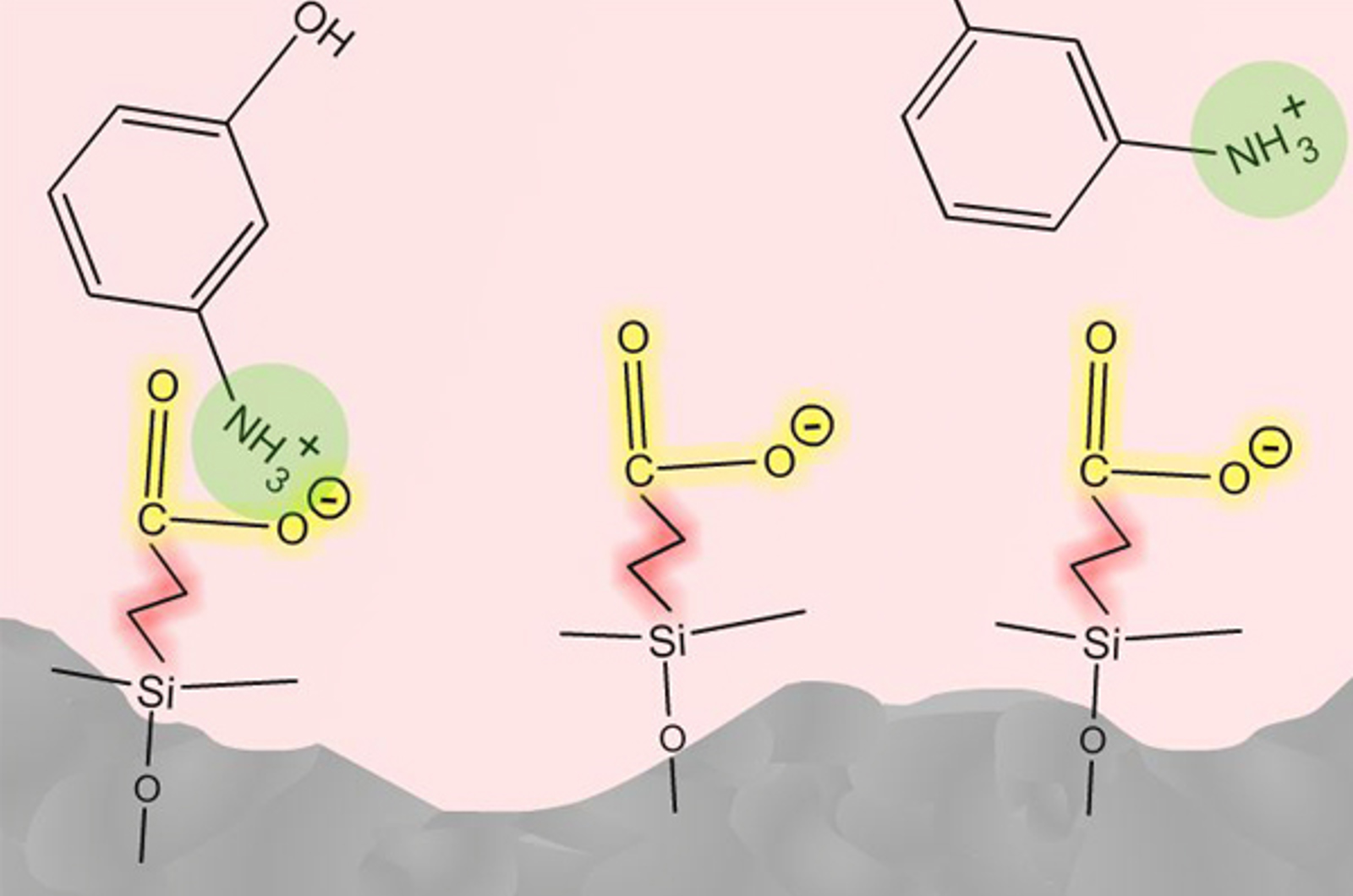
HPLC – Ion Chromatography
Ion chromatography encompasses many different chromatographic mechanisms and techniques, all of which can be applied to the separation of ions or ionizable analyte molecules. This short video will introduce some of those techniques as well as method parameters which are applicable for the modification of analyte retention characteristics.
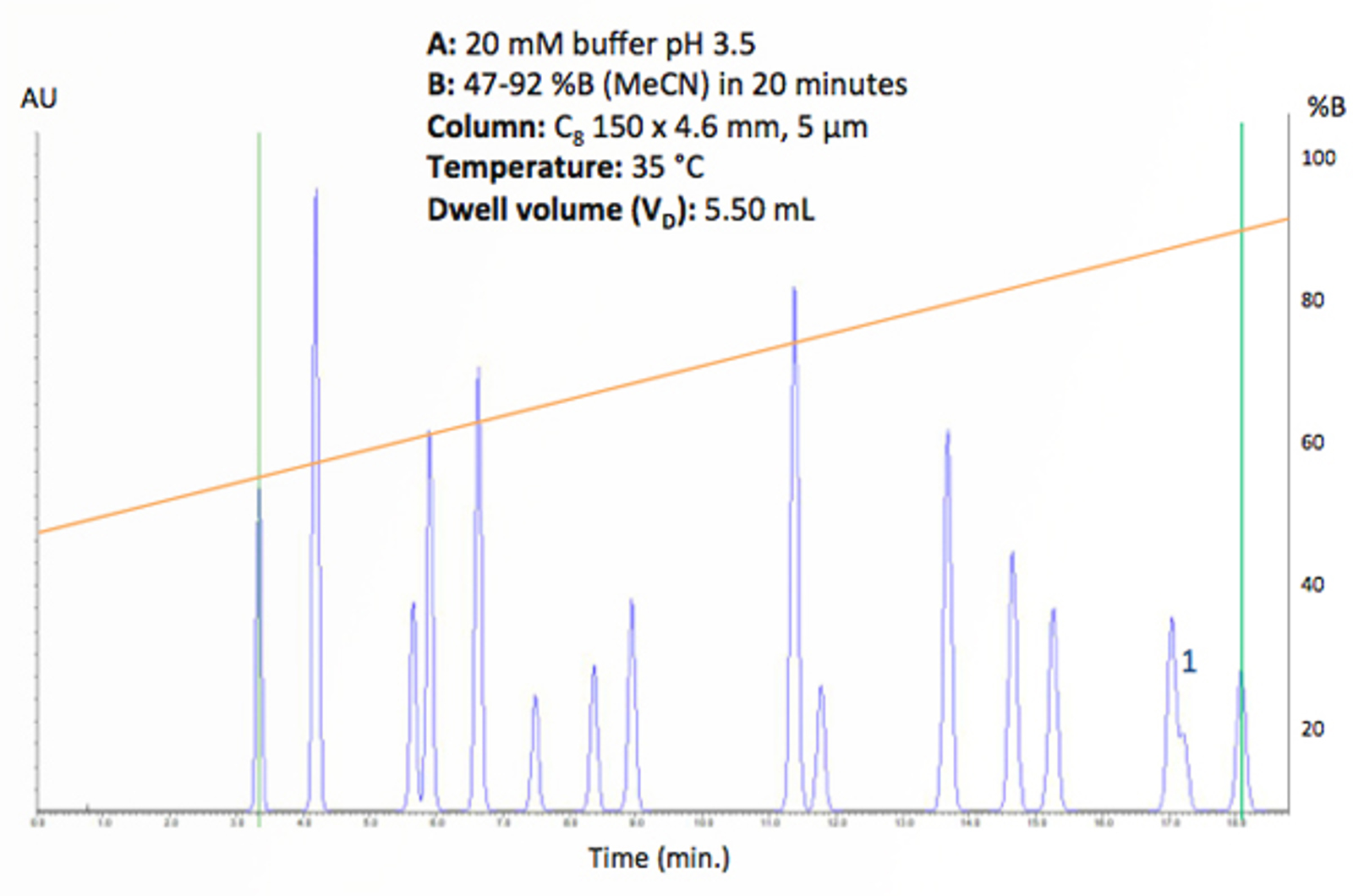
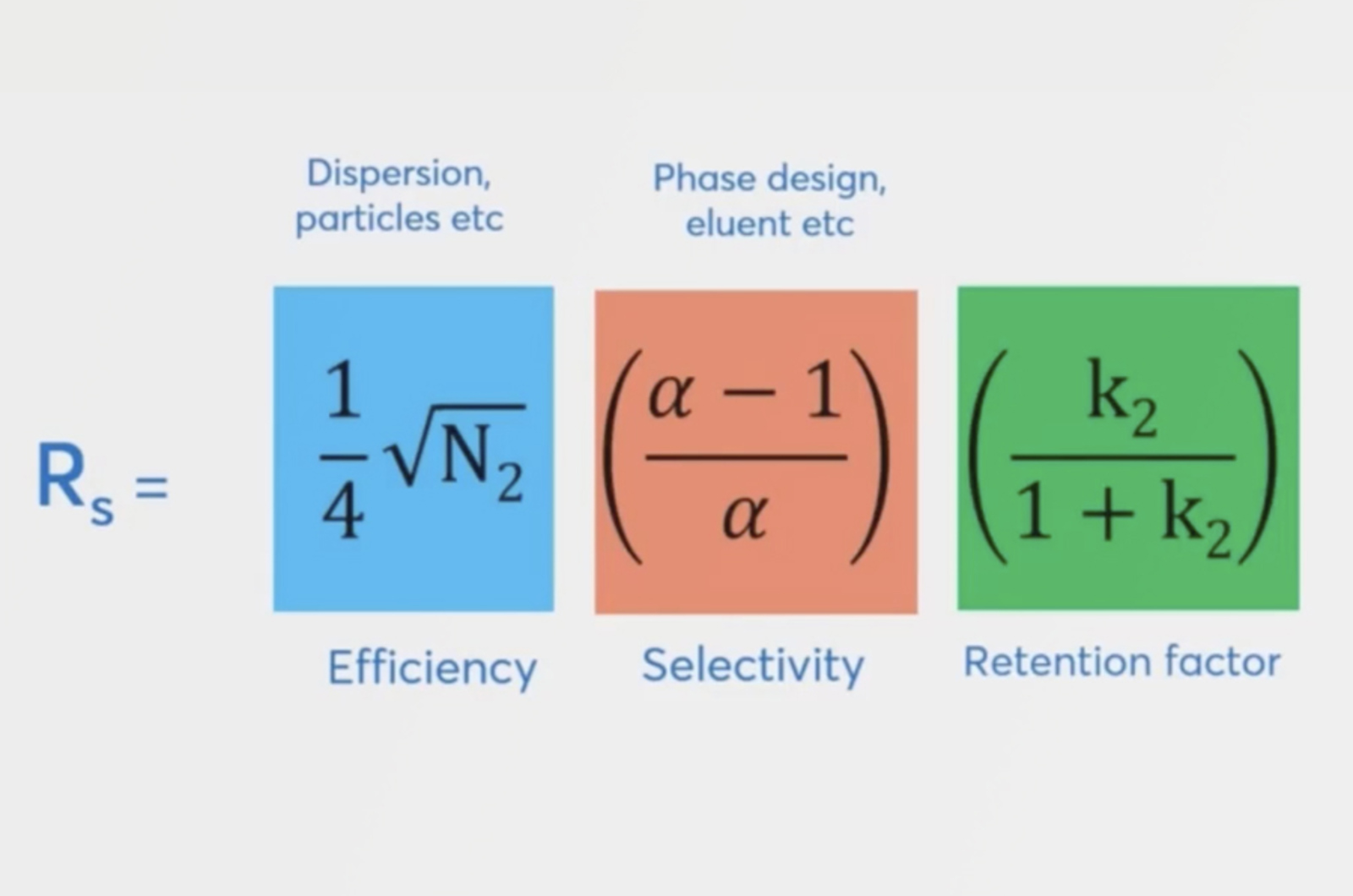
Optimizing Gradient HPLC Parameters
Gradient elution is an important technique for the separation of complex mixtures of analytes or for analytes with large molecular weights. There are several parameters which define a gradient separation, which should be considered and optimized. The following article will detail a few simple equations which can be quickly used in conjunction with a scouting gradient to produce a successful gradient elution.
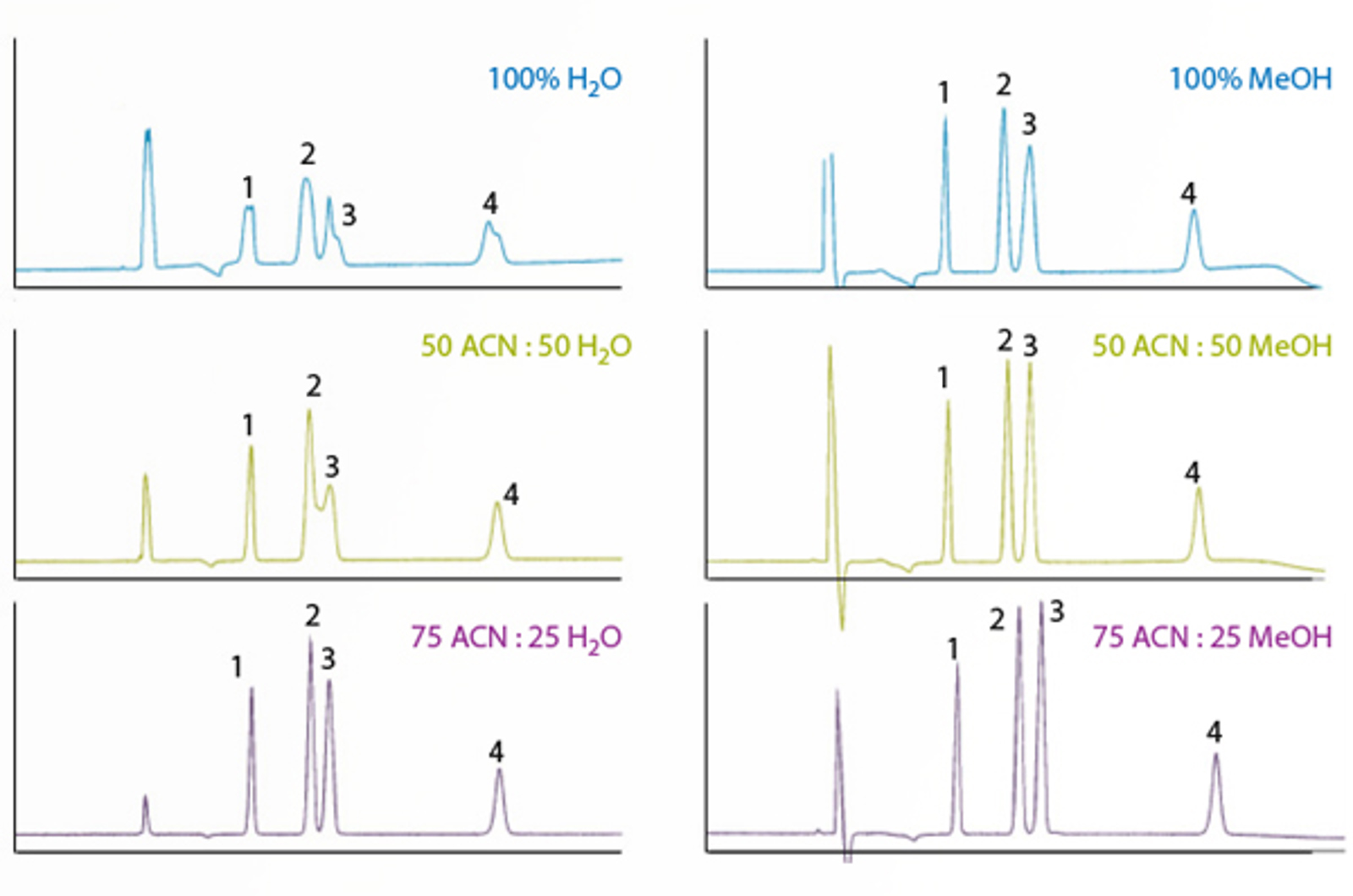
10 Tips for HILIC Mobile Phase Optimization
This quick guide lists 10 top tips to help optimize the mobile phase for HILIC separations.

Isocratic or Gradient?
You have been given a C18 column, an unknown sample and been asked to develop a reversed phase HPLC method. Where do you start? Do you use isocratic or gradient elution? Don’t panic! Let us make the decisions easy for you. Using the steps outlined and the example scouting gradient, we will walk you through the decision making process, taking all the stress and worry away for you!
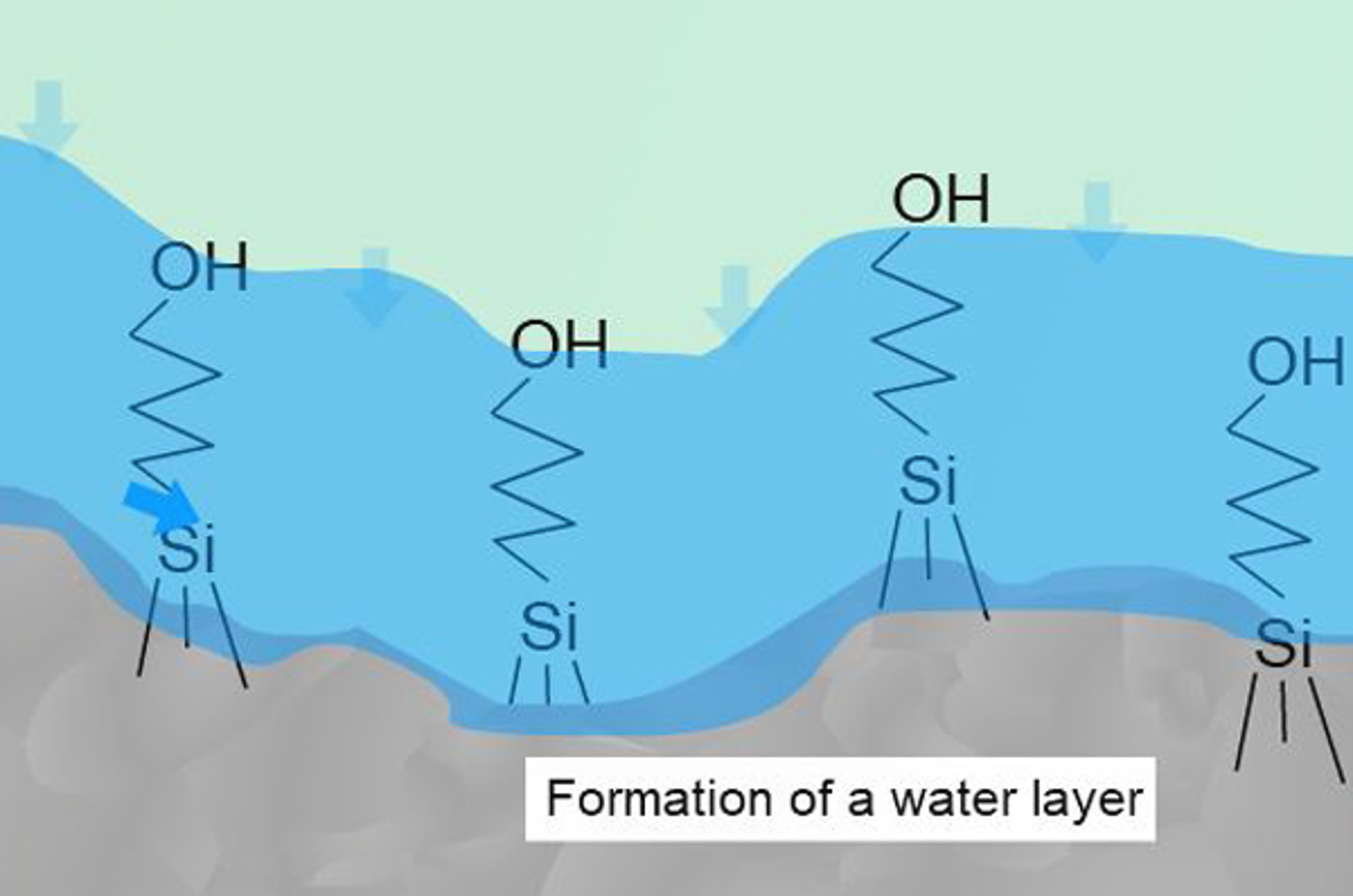
The Basics of HILIC
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) is applicable to the separation of very polar, highly water soluble analytes which are often poorly retained (if at all) under reversed phase HPLC conditions. In this quick guide you will learn about the basic science which underpins this powerful technique.
Understanding Gradient HPLC
In this session, our speakers present a definitive guide to using, optimizing and troubleshooting gradient HPLC. The session will consider key topics such as the mechanisms of gradient HPLC versus isocratic elution, developing robust gradient HPLC methods, the dangers of altering column flow or column dimensions without proper gradient scaling and the essentials of troubleshooting gradient issues.
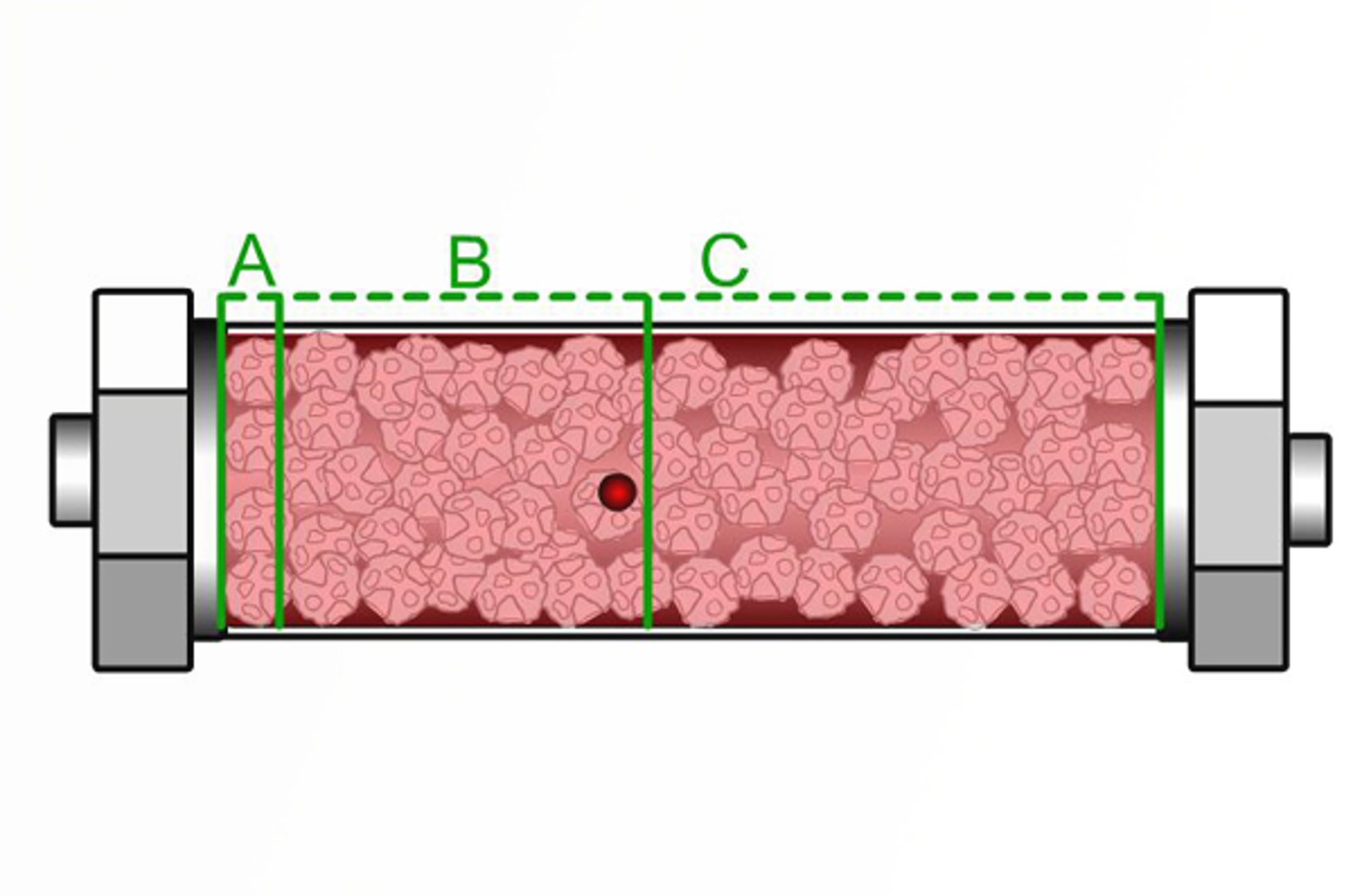
HILIC Conditioning and Equilibration
Conditioning and equilibration are important for many HPLC methods to avoid inconsistent retention times between analyses. Particular consideration has to be given to HILIC methods due to the mechanism of analyte retention via an adsorbed water layer at the stationary phase surface. This quick guide will provide you with some practical information on where to start with HILIC column conditioning and equilibration.
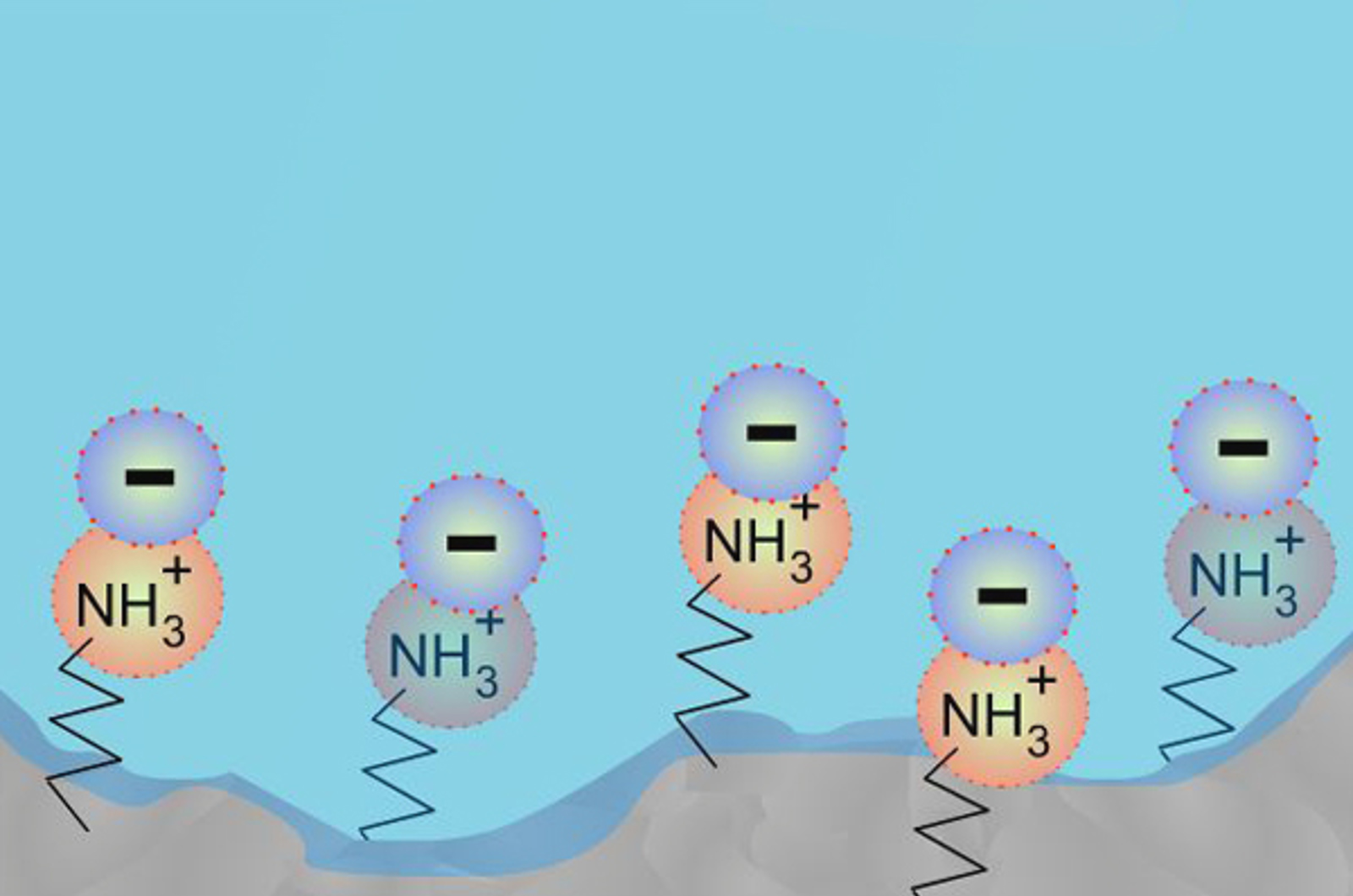
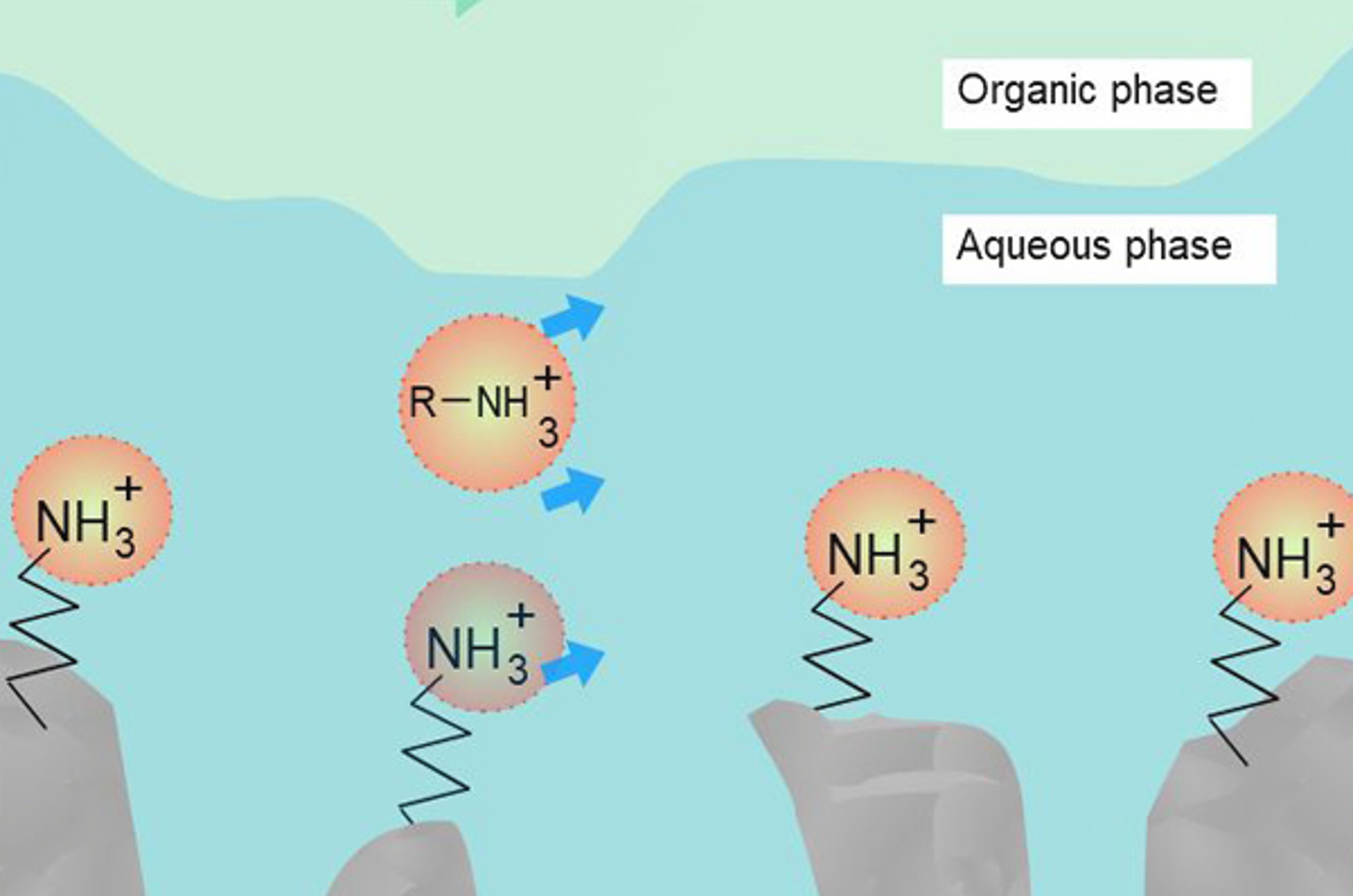
Making HILIC Work for You
This webcast will provide you with the tools you require to understand and design HILIC methods. Understanding the importance of stationary phase choice and how organic solvent, salt content, pH, and column temperature can effect separations will ensure method development is streamlined and the resulting methods produce robust results.
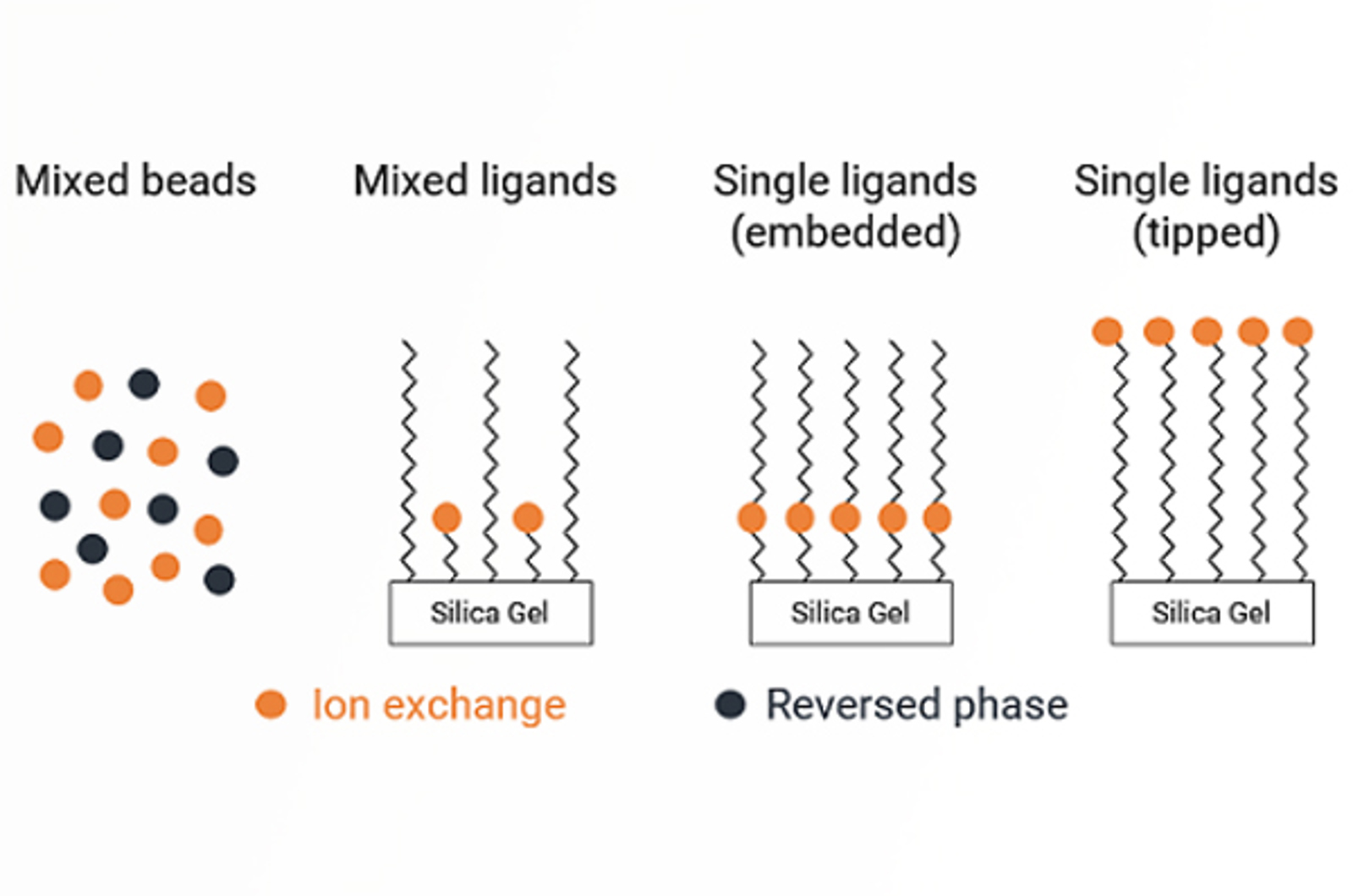
Mixed-Mode HPLC
This module discusses the primary modes of retention which must be understood to successfully develop mixed-mode separations. Each method parameter, how it is altered, and the effect it has on the resulting chromatography is discussed. We will also provide you with a method development strategy which can be applied to separations.
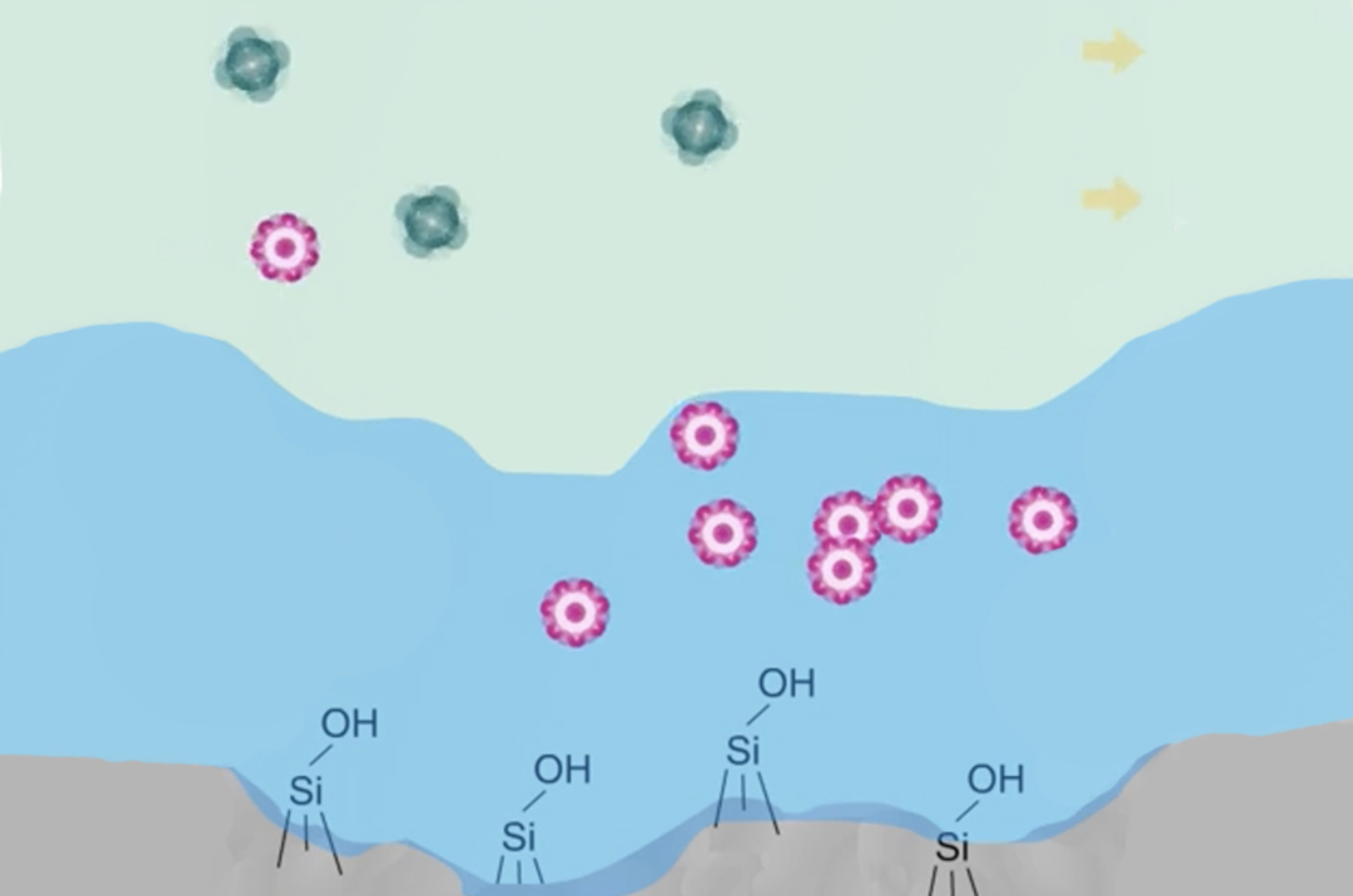
Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) and Related Techniques
This webcast presents a comprehensive review and tutorial on hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC). This technique is very useful for retention and separation of polar and ionizable compounds and provides a very useful orthogonal separation mechanism for chromatographers. We include a comprehensive review of the mechanisms of HILIC separations as well as considering the major parameters which affect the separation selectivity including eluent solvent composition, pH, and buffer type and strength.
CHROMTalks HPLC Series
Highly experienced speakers from industry and academia take some time to discuss their past (and more recent) experiences with chromatography and impart their key learnings. From heroic failures that have taught them valuable lessons, to moments of inspirational serendipity, and everything in between, these relaxed, unconventional, and often humorous presentations will be invaluable to everyone working in separation science.
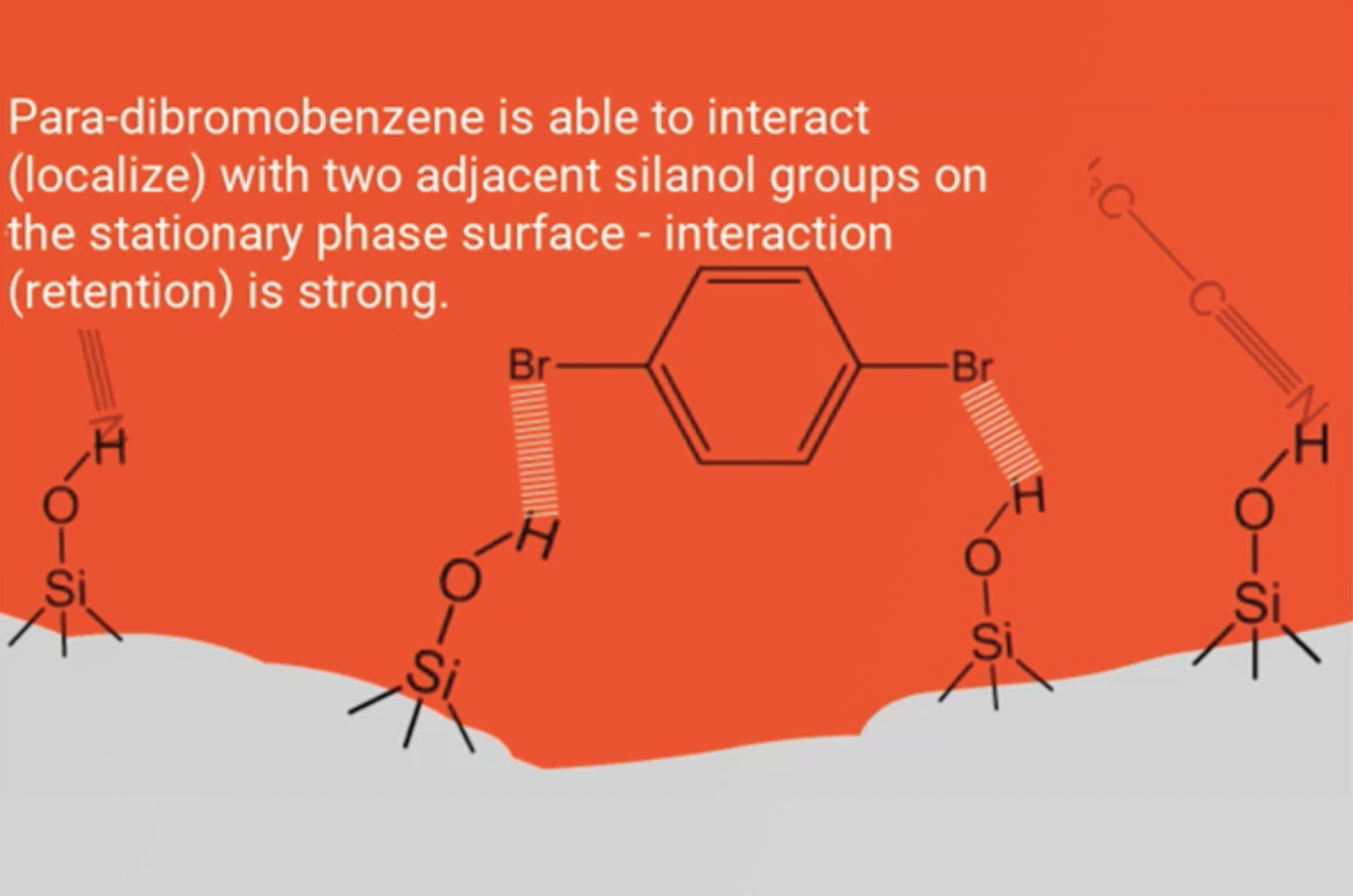
Normal Phase HPLC - Mechanism and Stationary Phase
Normal phase chromatography was the first liquid chromatographic technique reported. This short video will consider the primary retention mechanisms of normal phase chromatography, along with retention order and the stationary phases which are typically employed for normal phase separations.
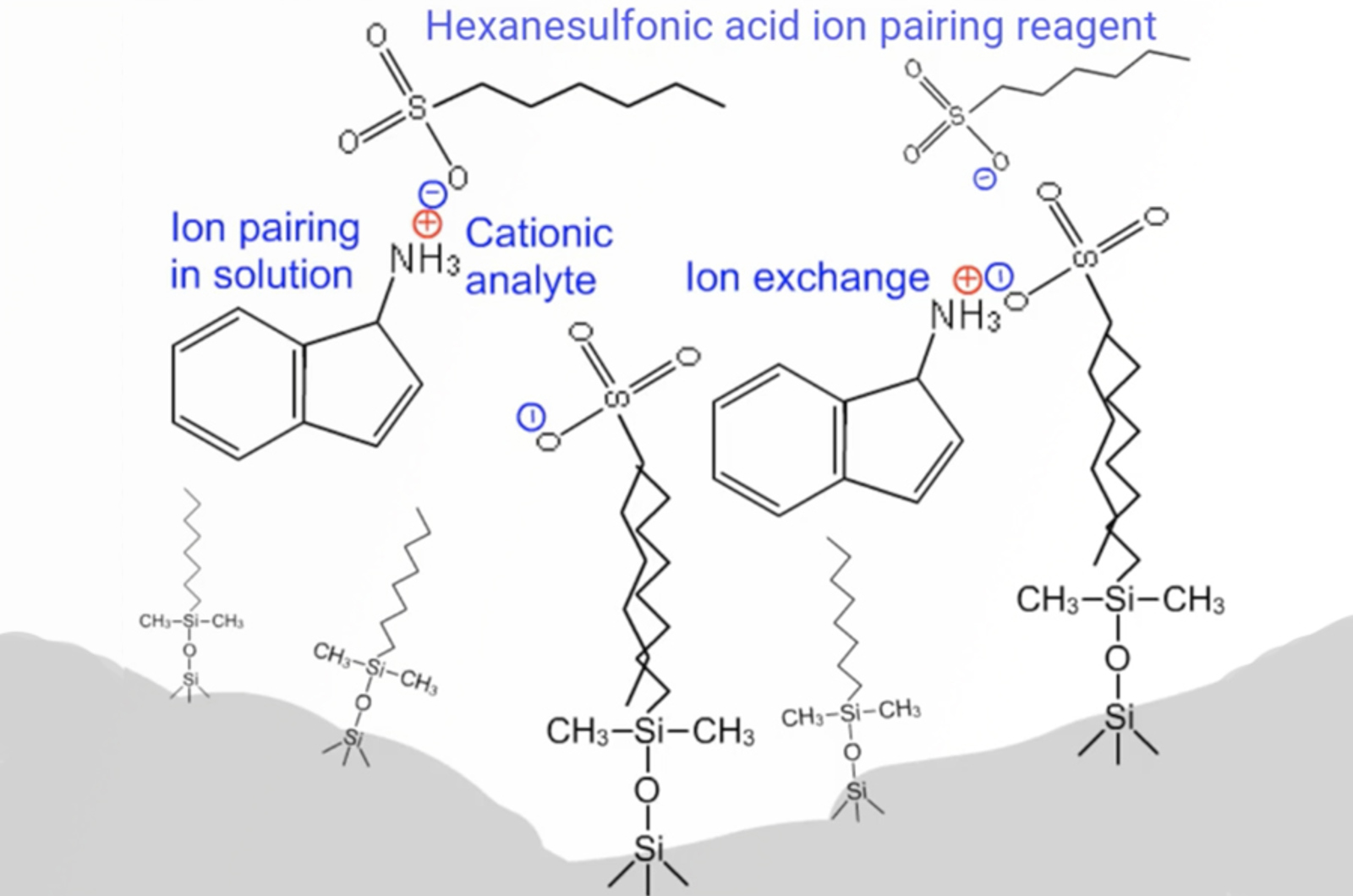
Ion Pair Alternatives
Ion pair reagents are useful to aid in retention and separation of ionizable analytes. However, they add another level of complexity to methods. Here are some alternatives strategies to consider prior to using an ion pair.
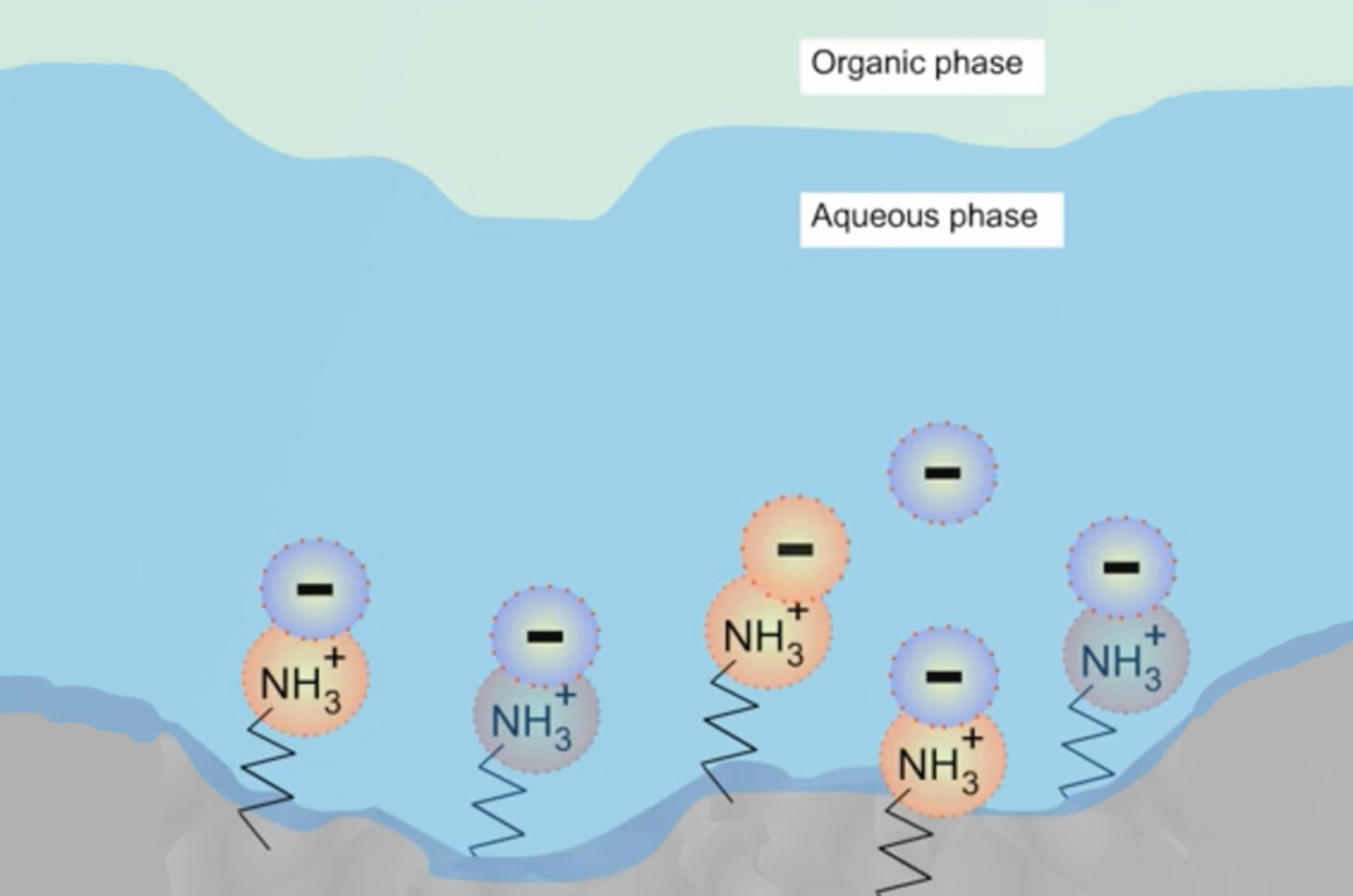
How to Choose a Stationary Phase for HILIC
HILIC requires a hydrophilic stationary phase to adsorb a water layer in order to allow the analyte partitioning process to take place. This quick guide will give you a practical approach to choosing a HILIC stationary phase.
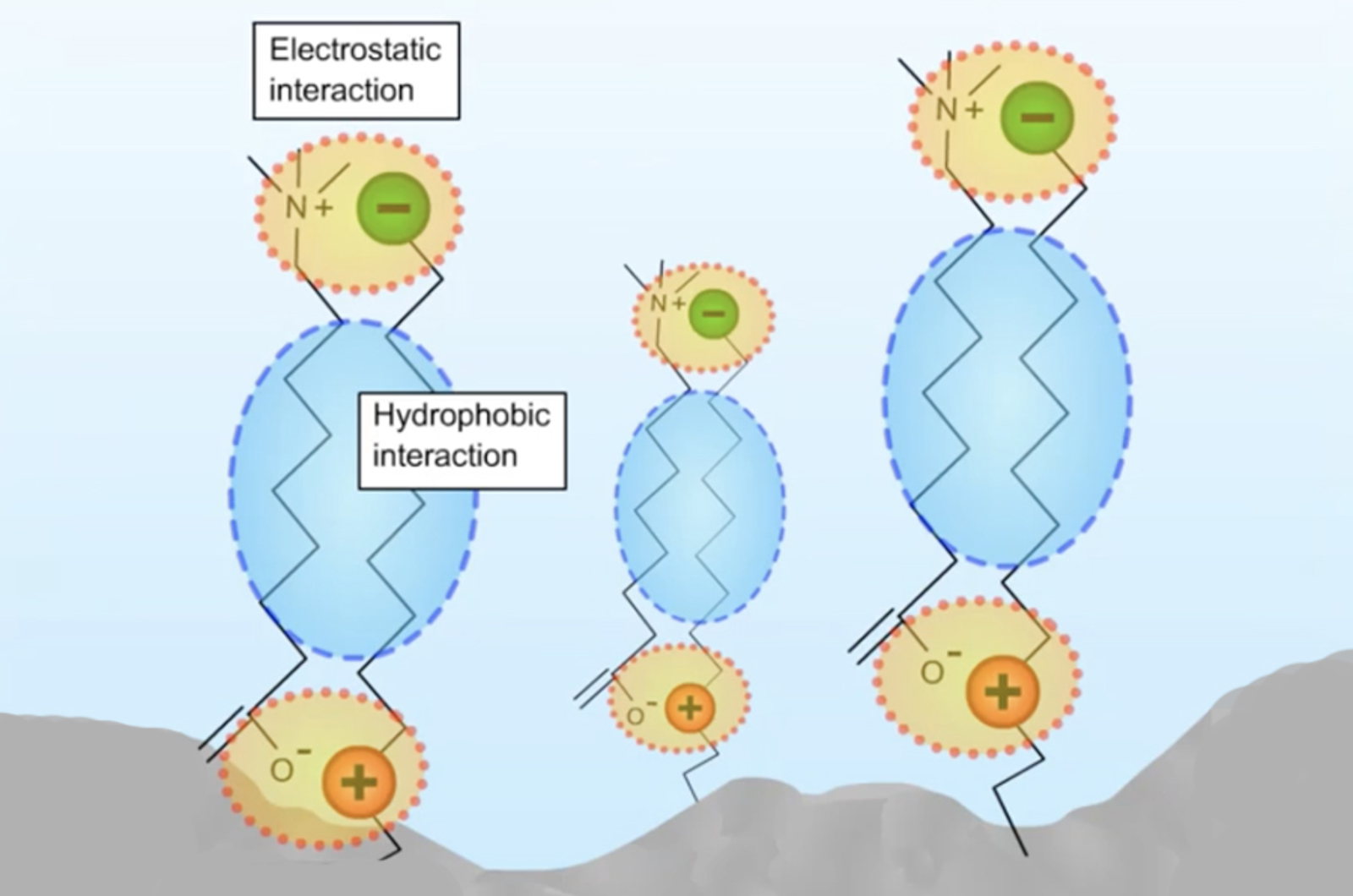
HILIC Mechanism and Stationary Phase
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) is a type of chromatography based on a mixed-mode of retention mechanisms. It has found utility in many application areas, but in particular is very applicable to the retention of highly polar molecules which exhibit poor retention characteristics under reversed phase HPLC conditions. This short video will teach you about the primary retention mechanisms and stationary phase interactions involved in HILIC.
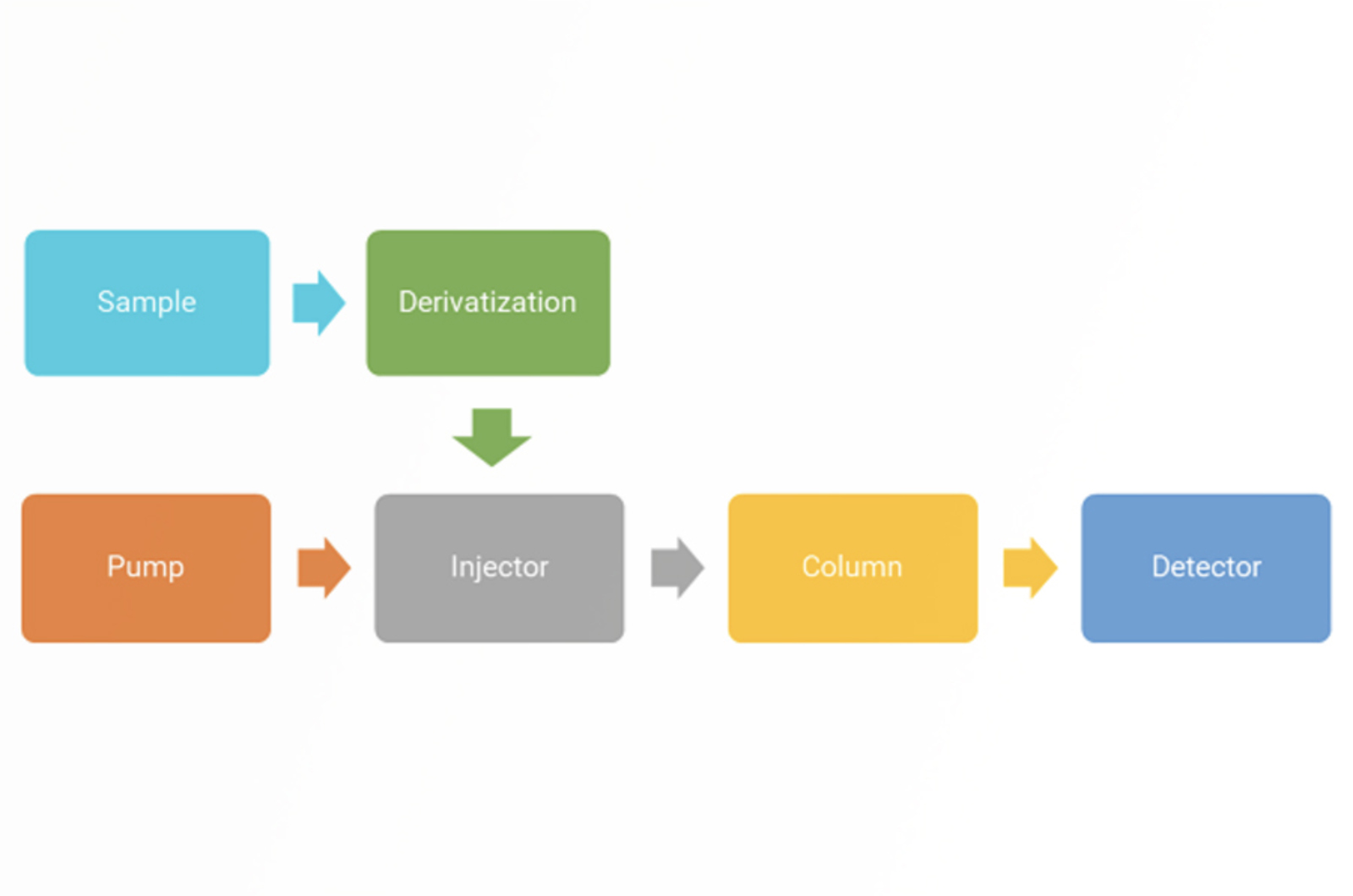
HPLC Derivatization
Derivatization of analyte molecules in HPLC is primarily used to improve and/or allow detection; in particular for molecules which posses no (or weak) chromophores, fluorophores, or electrophores. Derivatization will inherently add time, complexity, and cost to the analytical workflow, however, this quick guide will help to determine if derivatization is suitable for your application by considering reasons for implementing derivatization and how this can be done.

Practical HPLC Video Bootcamp
Join us for a little over an hour on this step-by-step guide through setting up an HPLC instrument. Avoid common errors and pitfalls and understand every step of the process to get your instrument set up correctly every time, decrease down-time, and reduce the risk of re-analysis.

HPLC Method Review and Workload Planning
In this module an experienced analyst takes you step-by-step through the process of how we do this. We'll look in detail at every part of what appears to be a straightforward HPLC method, paying particular attention to the many areas which carry a high risk of error and how we can plan our work to minimize many of these common errors.
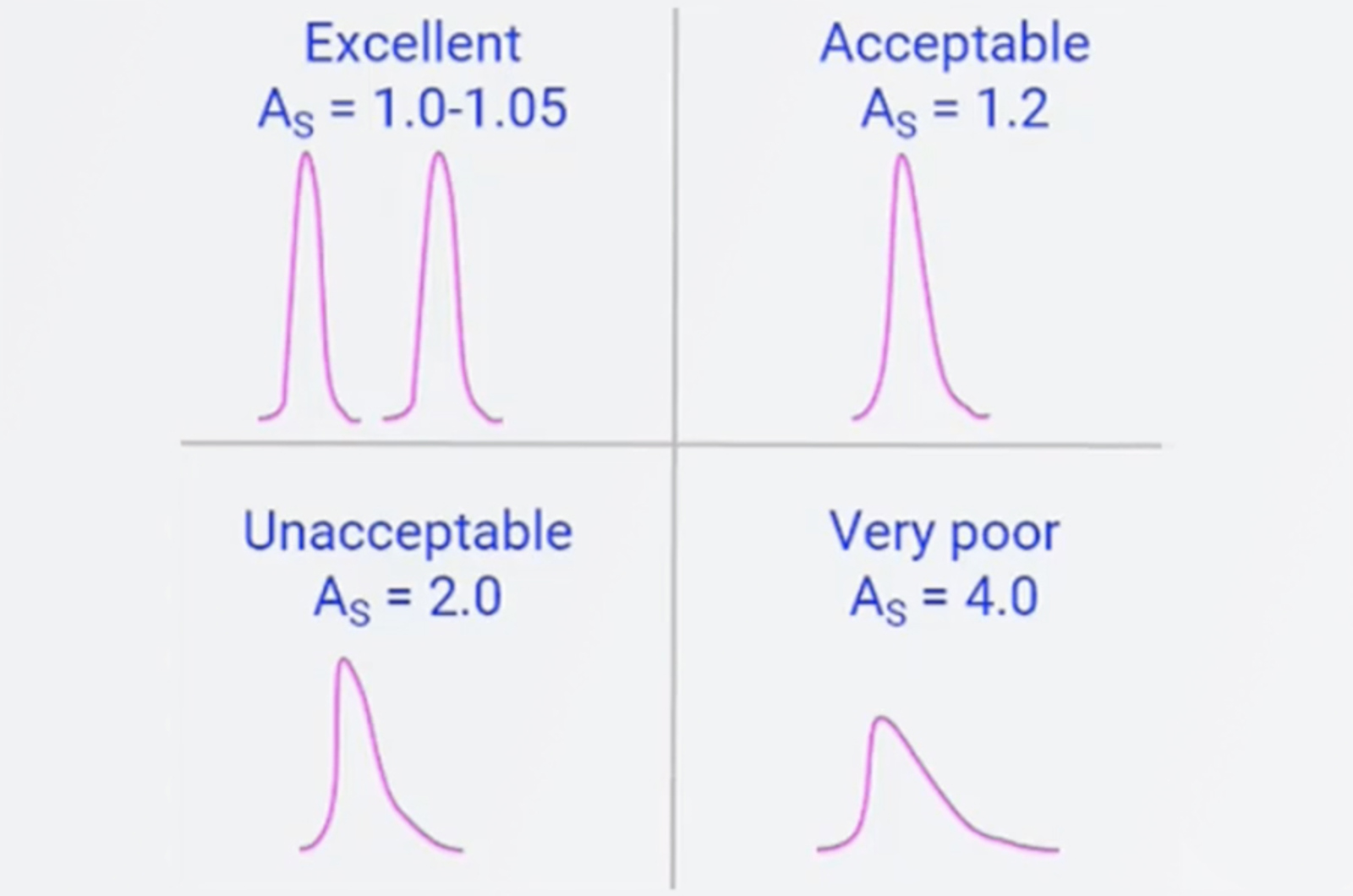
System Suitability for HPLC
System suitability is a series of checks built in to a sequence to ensure all sample data is correct and valid. This webcast will describe how we design and perform system suitability and which chromatographic parameters we should be assessing during the process.
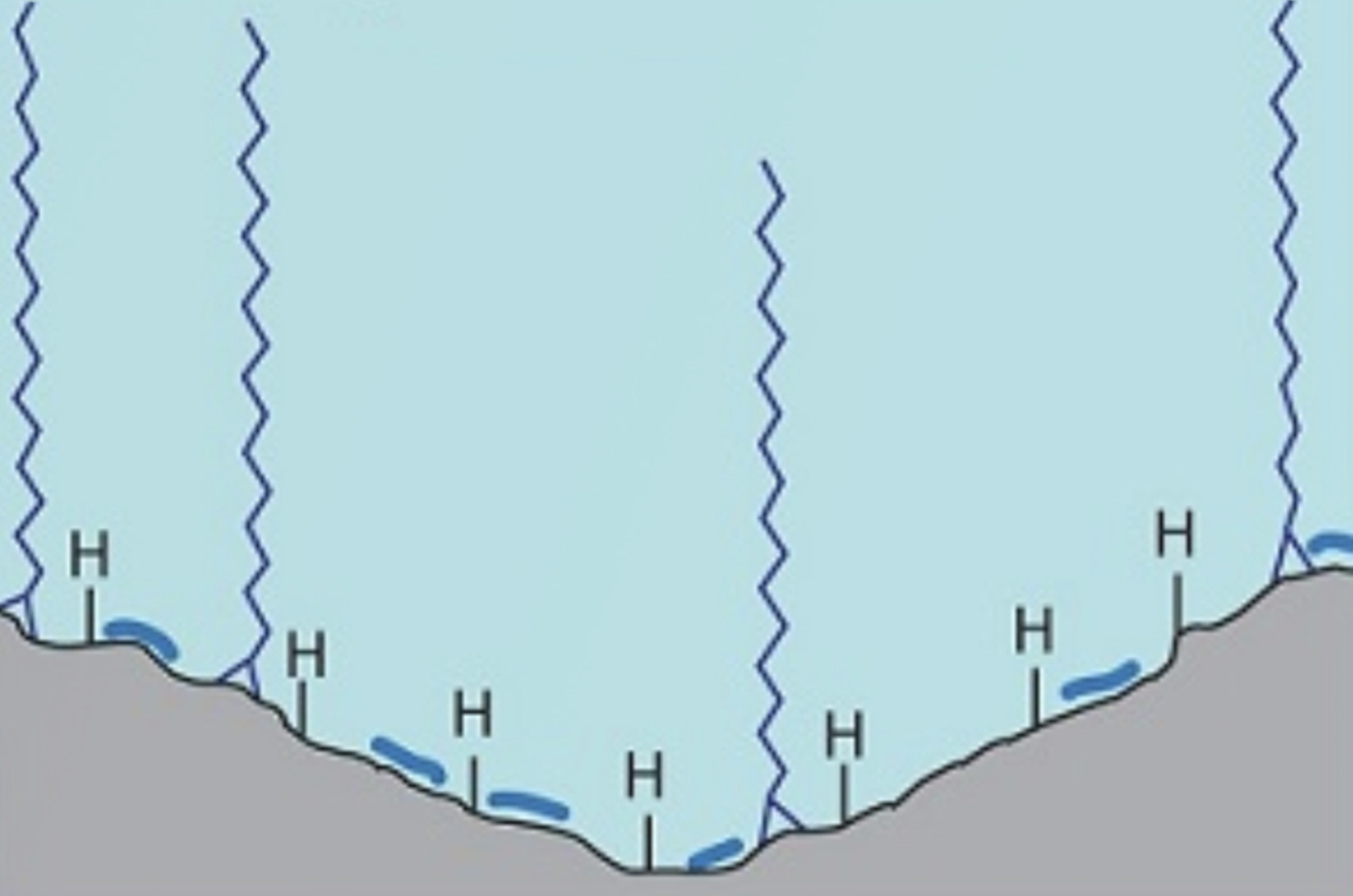
Aqueous Normal Phase (ANP) Chromatography
This module describes aqueous normal phase (ANP) chromatography, a unique high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) retention mechanism. Every chromatographer is familiar with reversed phase (RP), organic normal phase (ONP), hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC), and ion exchange modes of HPLC.
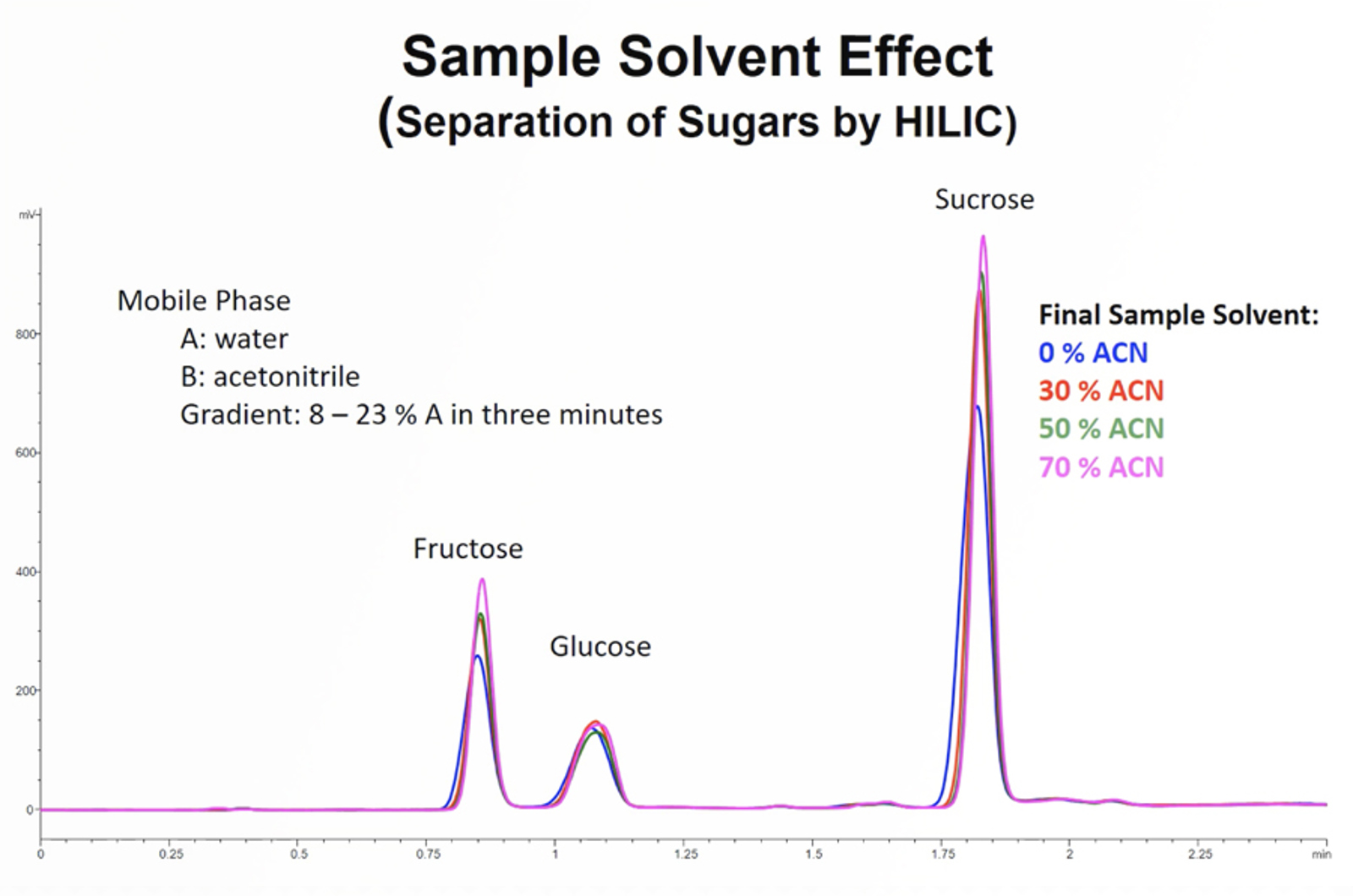
CHROMtalks - Key Issues with Sample Preparation for Liquid Chromatography
In this presentation, we will look at relationships of solvent selection considerations with peak shapes and injection considerations (solute focusing) and other serious chromatography offenses created by poor sample preparation considerations.
What HPLC Operators Need to Know Part 2: Column Selection, Mobile Phase Gradients, and Detectors
This webcast starts with column selection probably one of the most important choices in any chromatographic method. We will share our insights on how to select the correct column each time covering particle size, morphology, physicochemical properties as well as stationary phase selection. Finally, we will detail how to utilize and optimize HPLC gradients and review the various detectors available and when and how they are best employed.