Instrumentation
Optimize your HPLC instrumentation skills with expert training on pumps, autosamplers, detectors, and system maintenance. Learn how HPLC pumps regulate flow rates and pressure for precise separations. Master autosamplers to enhance sample injection accuracy and reproducibility. Explore detectors, including UV-Vis, fluorescence, refractive index, charged aerosol, and evaporative light scattering, for reliable compound identification. Our video tutorials provide step-by-step maintenance guidance, helping you troubleshoot issues and extend instrument lifespan. This interactive training includes real-world applications, animations, videos, and quizzes. Ideal for professionals in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food safety, and environmental analysis, CHROMacademy helps you master HPLC instrumentation with confidence.
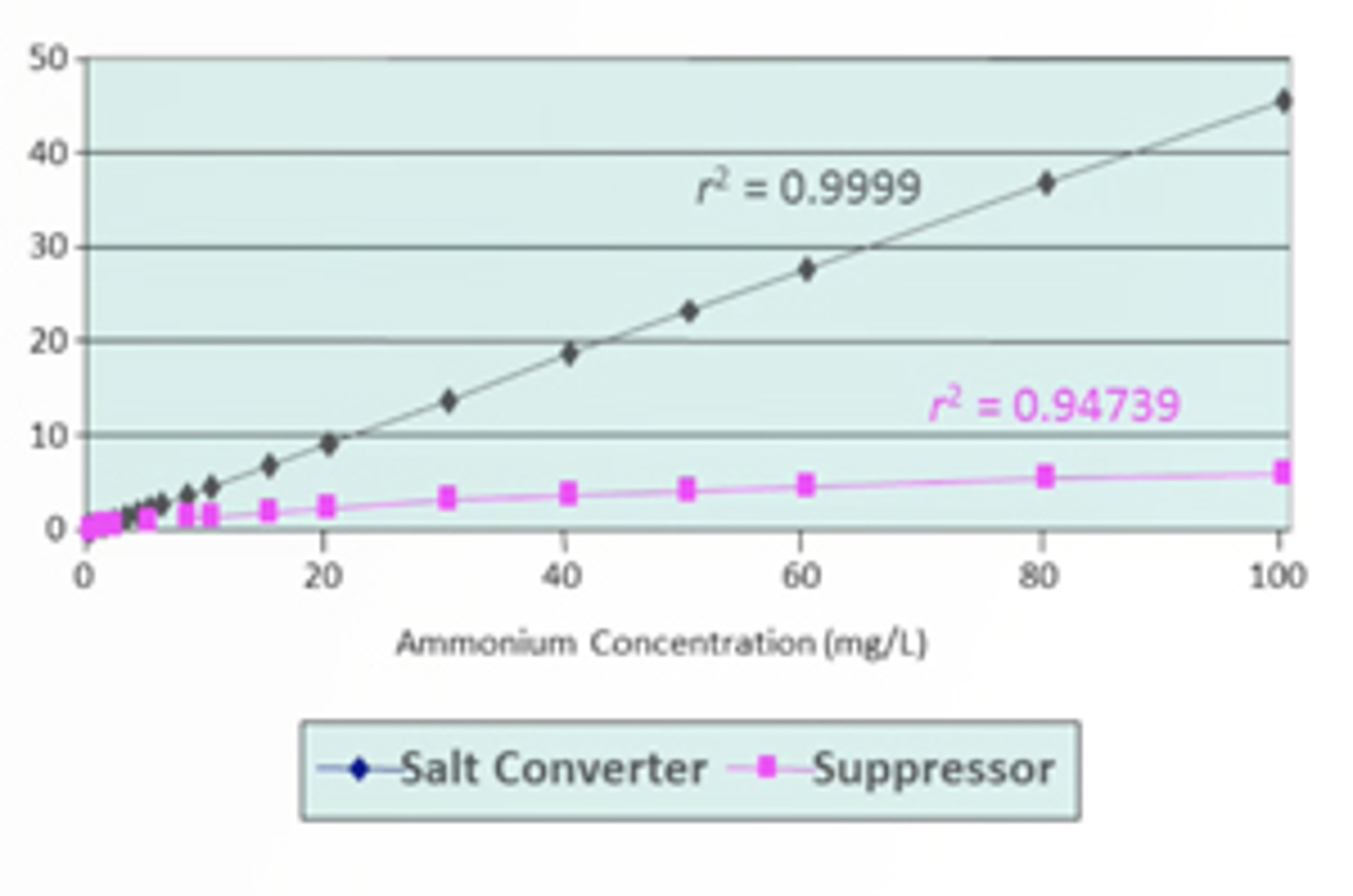
Conductivity Detection for Cation Chromatography - Advantages and Disadvantages of Suppression
Conductivity detection is separated into two applications: suppressed and non-suppressed. There is universal agreement in the analytical community that suppressor systems are necessary for sensitive and specific anion exchange chromatography. For cation exchange chromatography, there is still an ongoing discussion about if a suppressor system is required.
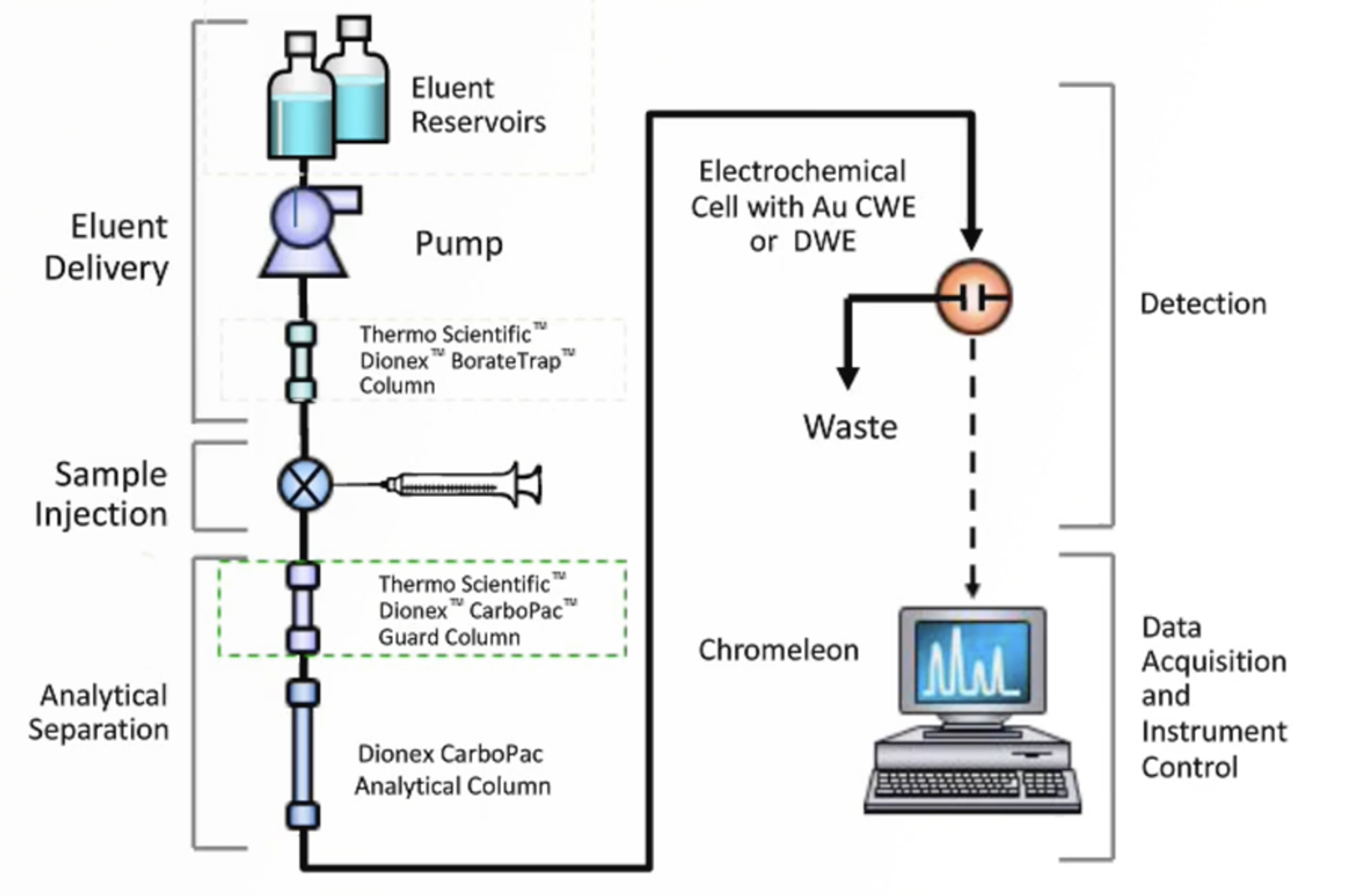
Tips and Tricks for Carbohydrate Analysis Using HPAE-PAD
High performance anion exchange chromatography (HPAE) combined with pulsed amperometric detection (PAD) is a sensitive analytical technique for native carbohydrates without the need of derivatization. HPAE-PAD can be used to analyze mono-, oligo-, polysaccharides, and glycans. We will present tips and tricks so the system is optimal productive and will provide you the best possible results.
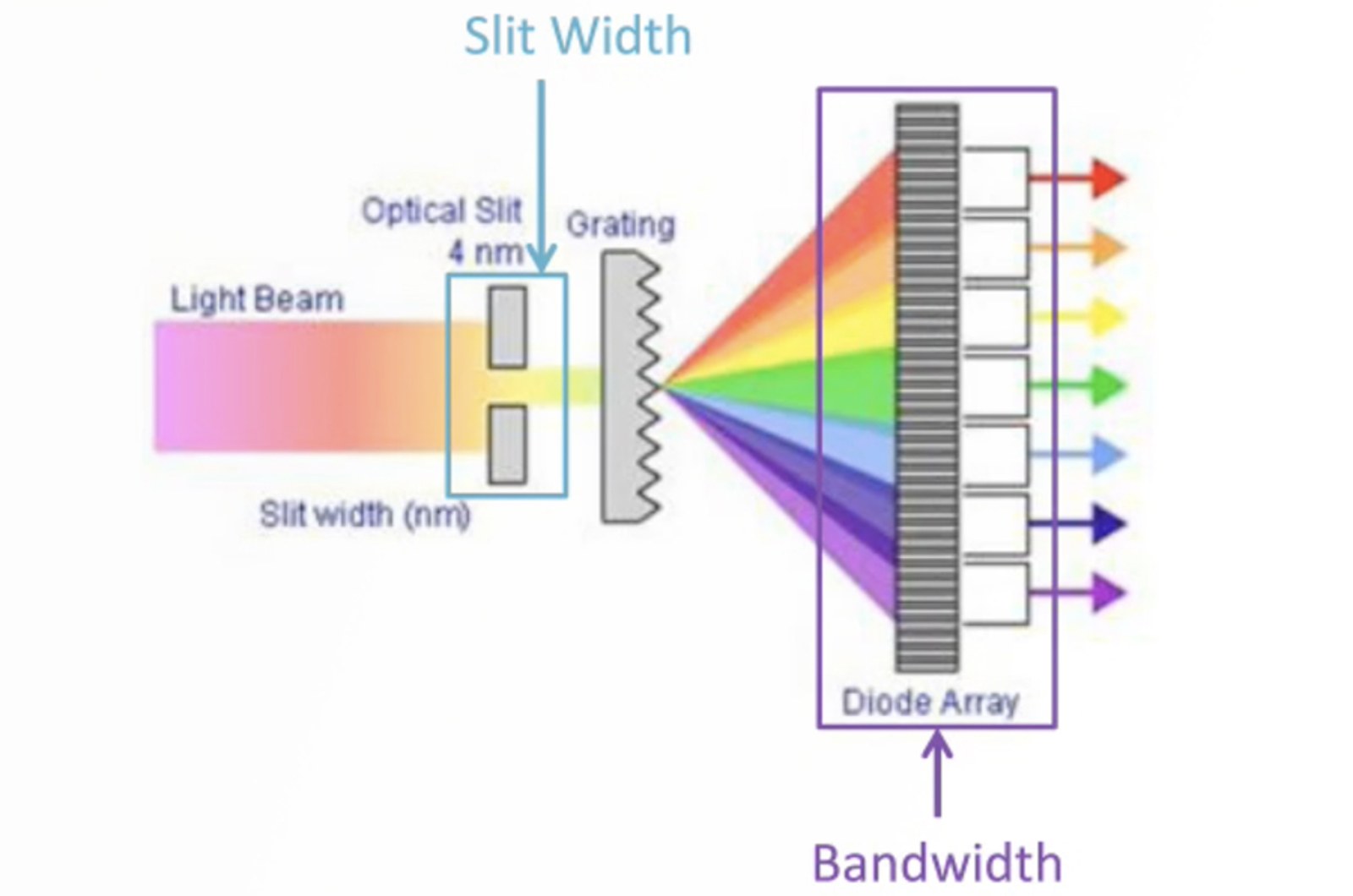
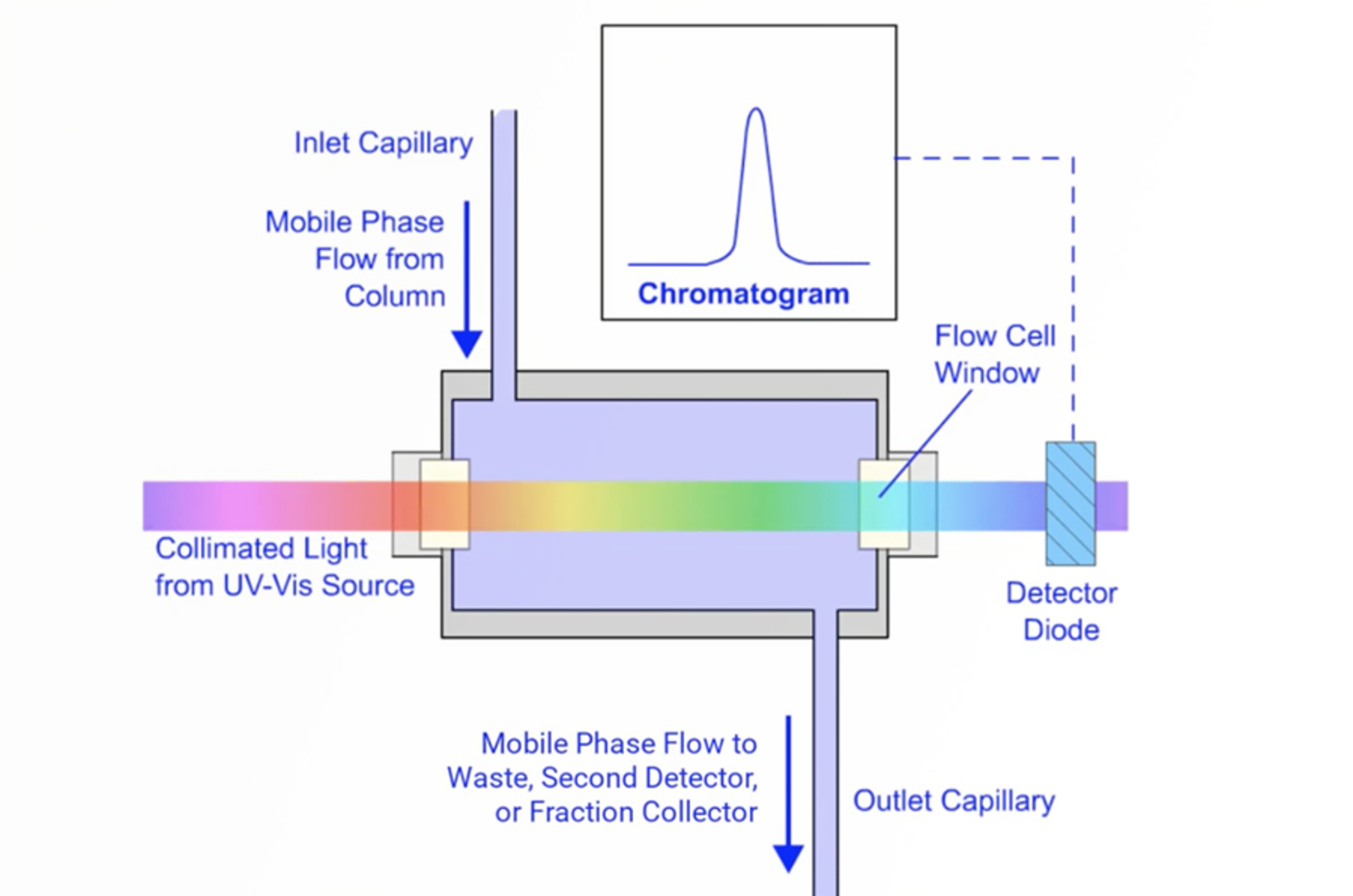
Everything You Should Know About UV Detection for HPLC
Key information on the instrumentation and the use and optimization of UV detectors for modern HPLC applications will be discussed. Important practical concepts will be explored and the optimization of each acquisition variable will be explained in detail in terms of both the instrumentation and chromatographic data sensitivity and specificity. Aspects of modern HPLC instrument design will be explored and related to improve chromatographic performance.
HPLC Detectors – What, Where, When, and How
This webcast will focus on the operation and optimization of the most common detectors. As well as considering the working principles of each detector we will discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and application areas for each detector type. This in-depth review of HPLC detectors will result in a better understanding of the operation, optimization, and detector choice for every application.
Everything You Need to Know About UV Detectors for HPLC
Get more from your UV detector by understanding how it works. The fundamental science behind UV detection and the working principles of this versatile detector will be discussed in detail. Optimization strategies for key parameters will be covered in order to provide you with the tools to correctly set up your detector to provide the optimum performance for your analytical requirements.
Autosamplers
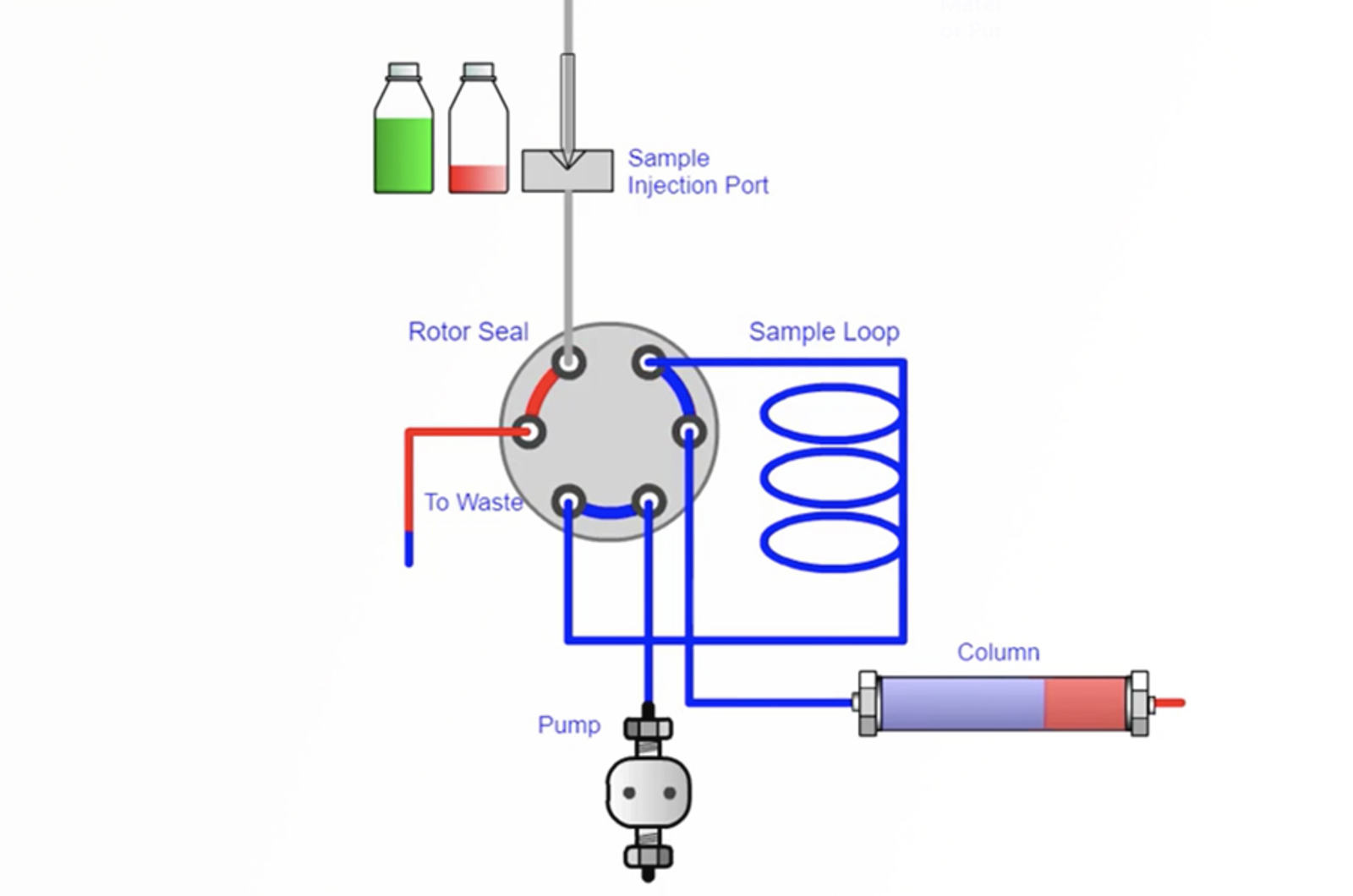
The aim of this module is to explain the purpose of injectors and autosamplers within the HPLC system. The principles behind which sample injection systems work will be described, as well as the individual components of an injection valve. The correct and incorrect ways to use loop injectors in manual injection mode will be highlighted, and we will discuss the major components and operating principles of a range of typical autosampler devices.
HPLC Solvent Pumping Systems
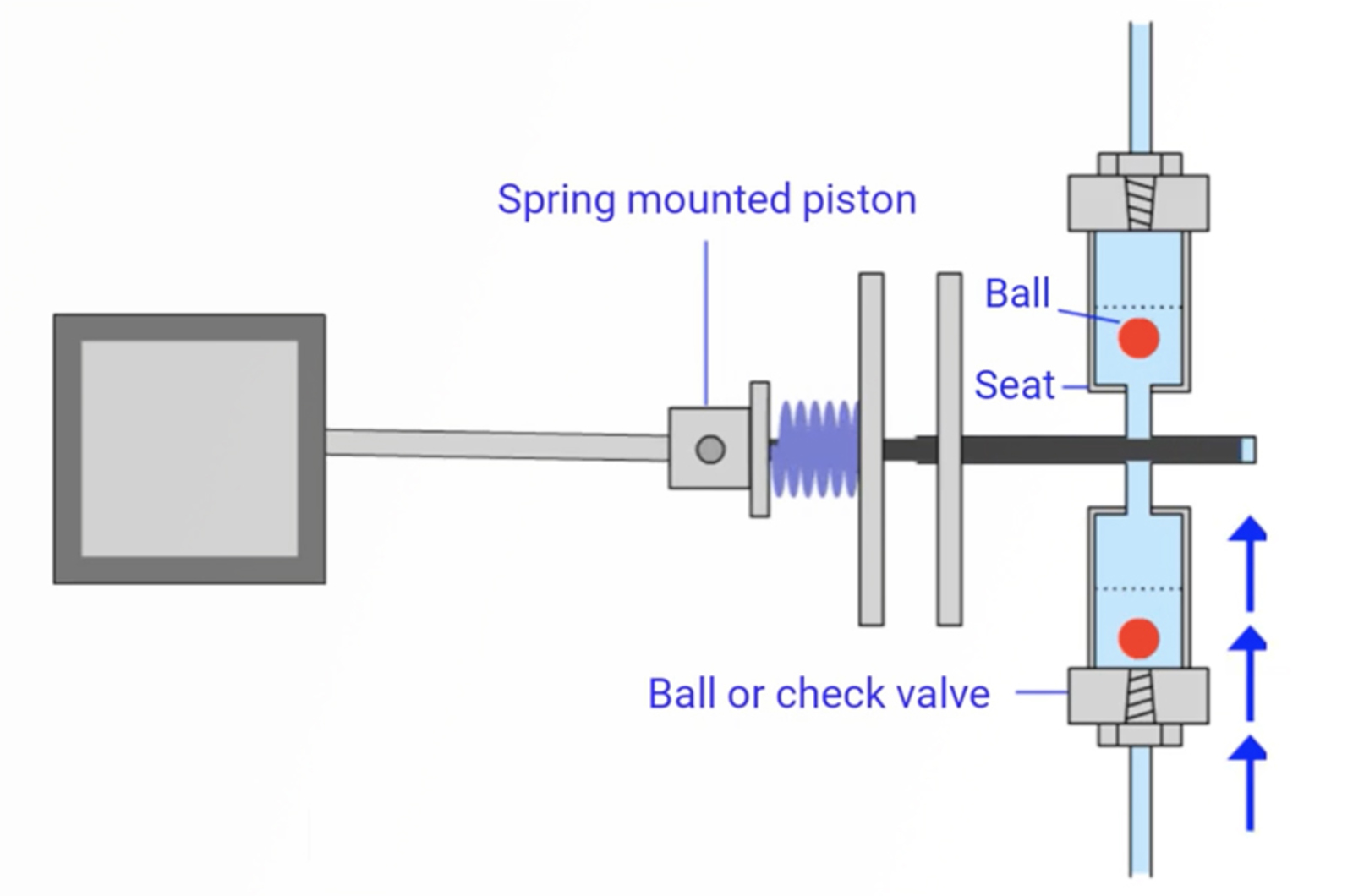
The aim of this unit is to describe the role of the solvent delivery system (pump) within high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC). The operational principles of the most popular solvent delivery types are explained, as well as the function of the components and potential troubleshooting and maintenance issues. We will describe good practice in pump use, care and storage, and discuss the operating principle of alternative pump designs such as preparative and micro-flow pumping systems.
HPLC Detectors
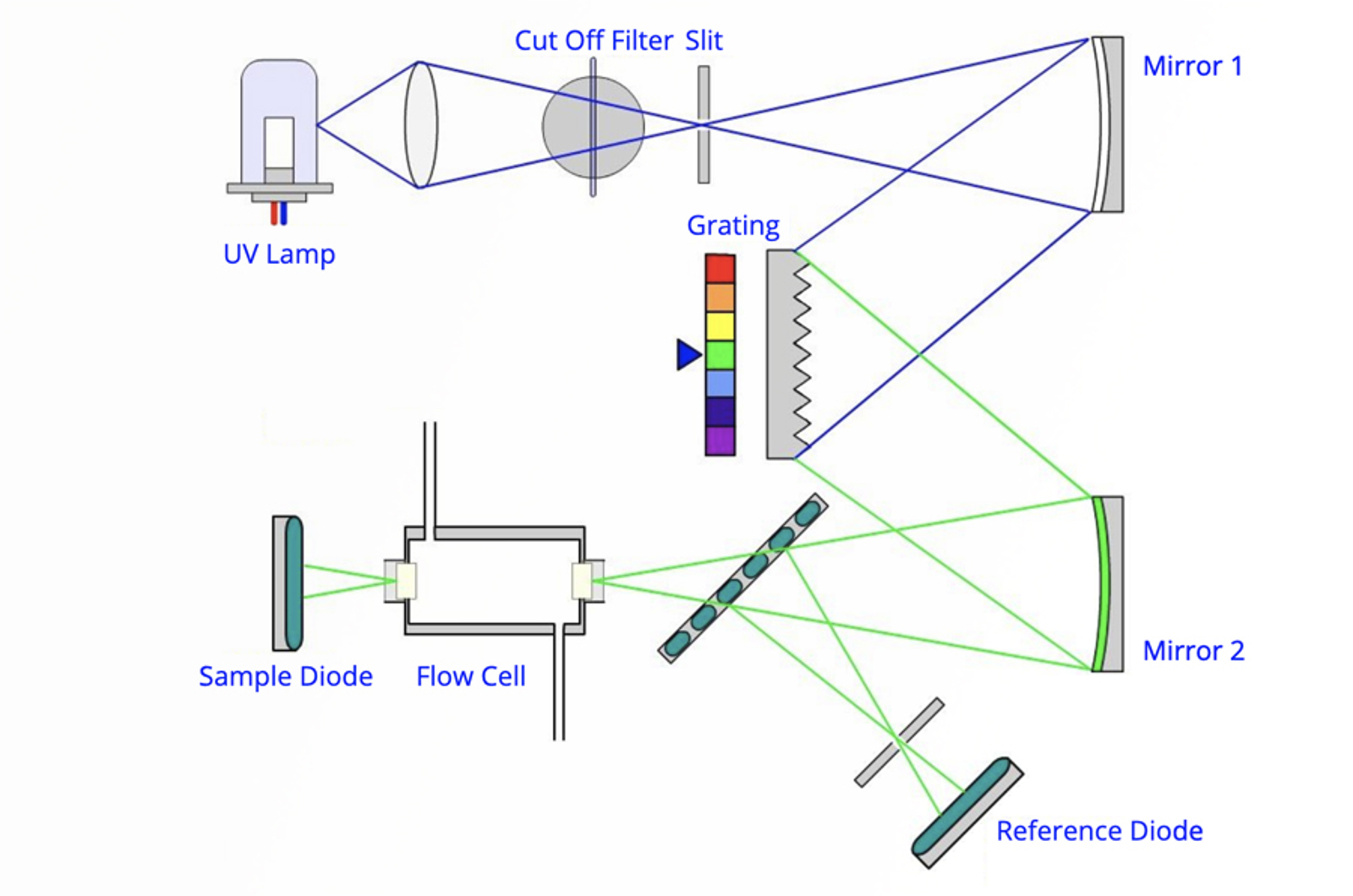
The aim of this module is to describe the purpose and general operating principles of detectors for HPLC. The general terms and concepts by which detector operation and performance are outlined. Specific operating principles of a range detectors for HPLC are covered, including UV-visible, refractive index, and fluorescence detectors.

Checklists Are Only for Pilots?
Try using the following checklist as an example before setting off a run on a UV HPLC system.
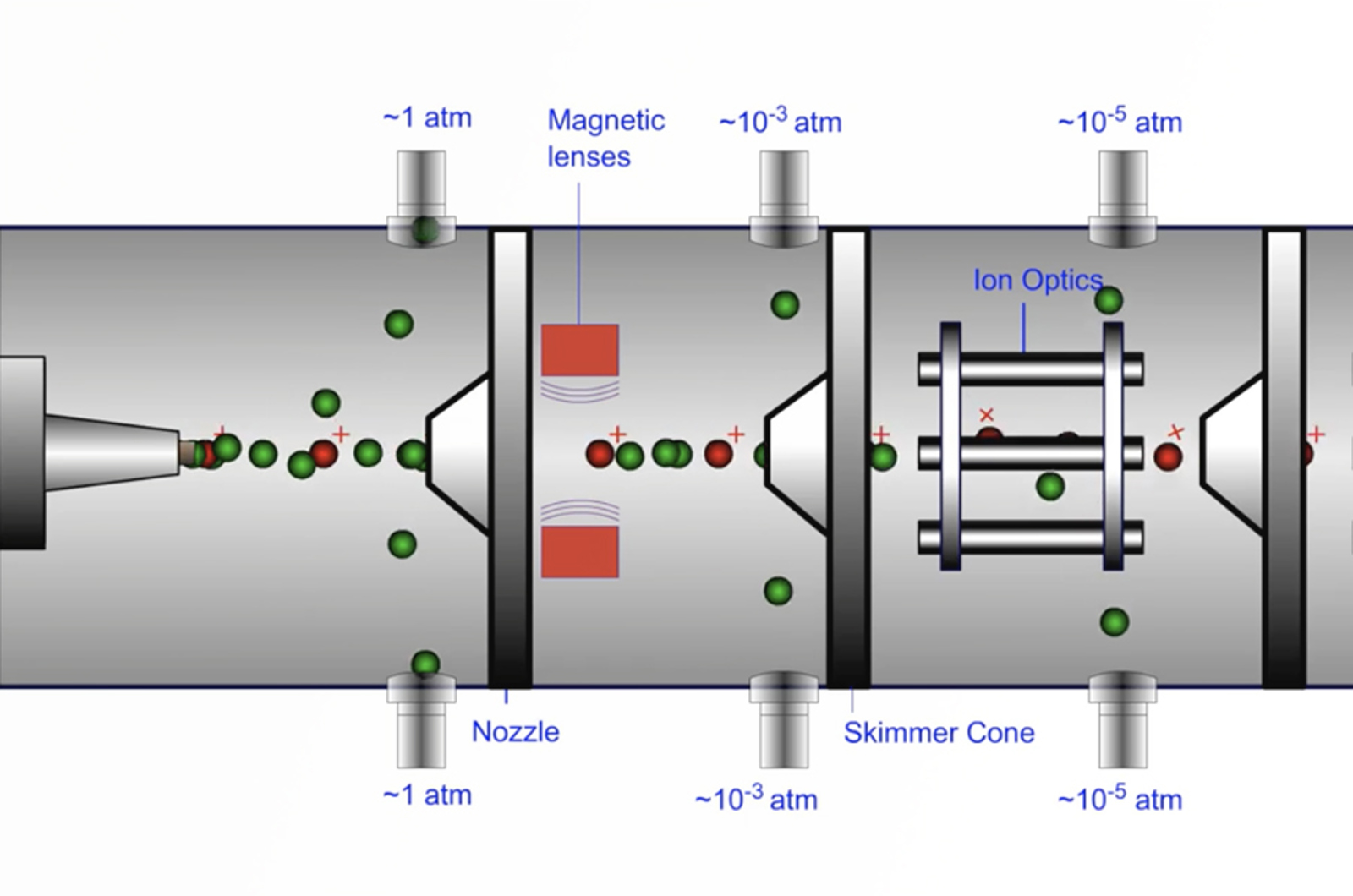
10 Good Reasons for Adding a Mass Spectrometer to My UV-HPLC
In this quick guide, we discuss the advantages of adding a mass spectrometer to UV-HPLC.
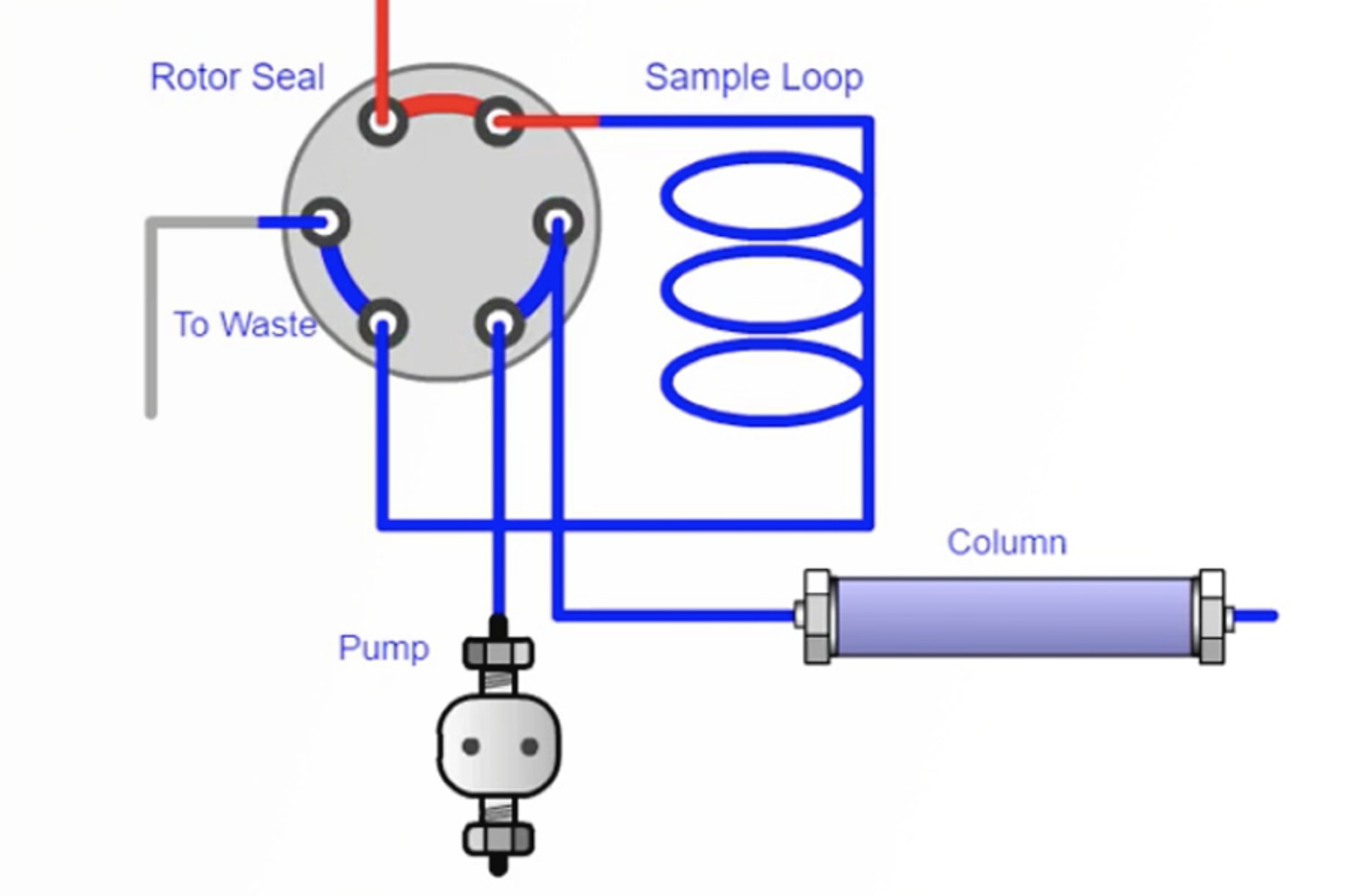
Autosampler Contamination
Contamination in any chromatographic method is a complex problem to troubleshoot. Extra peaks, often referred to as ghost peaks, in a blank or sample chromatogram can have a number of sources. This quick guide will focus on autosampler contamination, how to determine if the autosampler is the source, and how to remedy the problem.
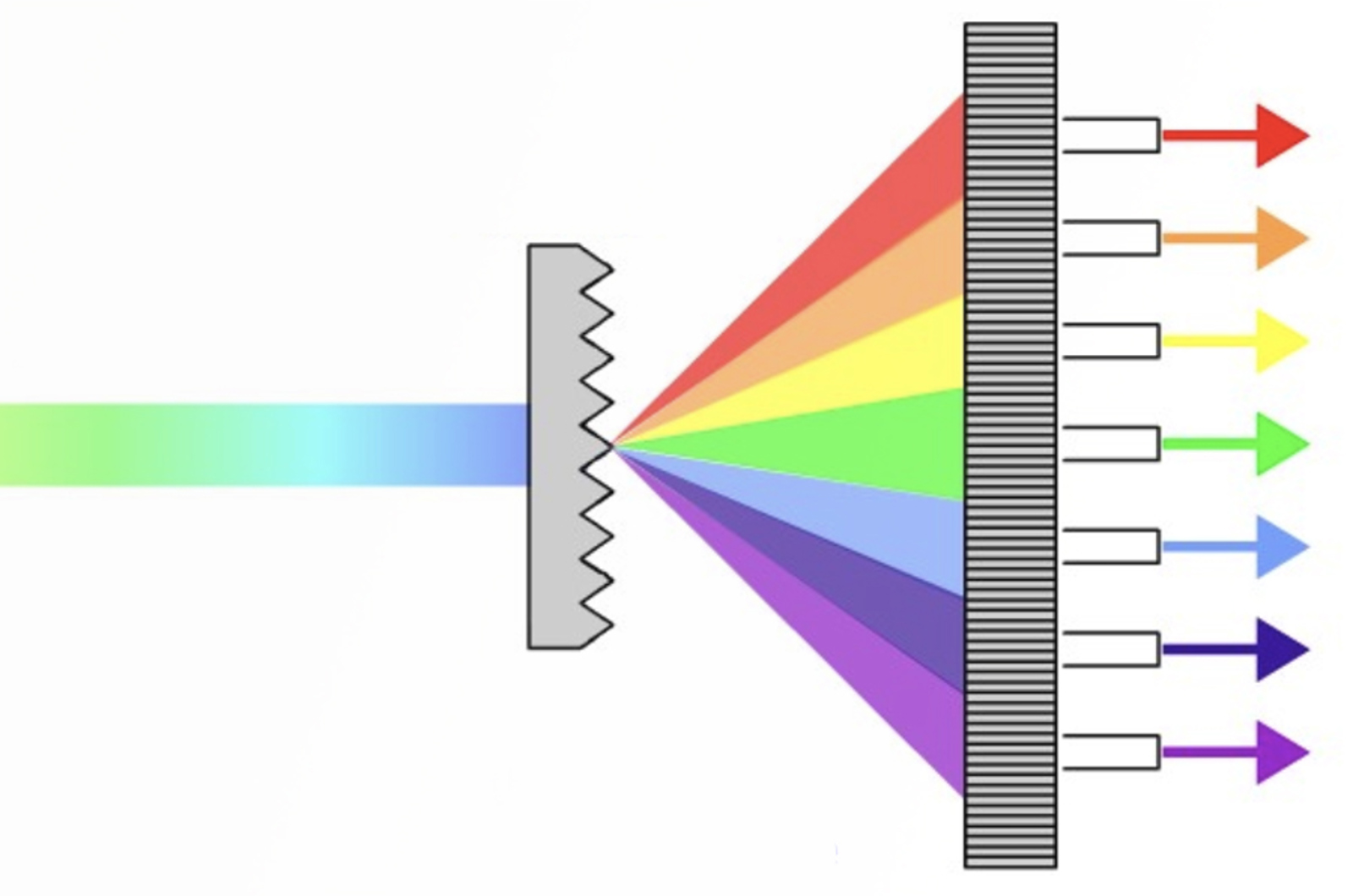
5 Diode Array Detector Settings That Should be Optimized
Don’t just set and forget your detector parameters. Let us help you make the most of your diode array detector (DAD) with our guide to the five settings that should be optimized, and our quick optimization tips.

HPLC Essentials - System Dwell Volume
One of the most common problems encountered when transferring a gradient HPLC method between instruments are irreproducible gradients and, therefore, inconsistent chromatographic results. This quick guide will provide you with all you need to know about system dwell volume.
HPLC Essentials - Switching Between Reversed and Normal Phase
A quick step by step guide to switching an HPLC between reversed and normal phase solvents. Get it right every time!
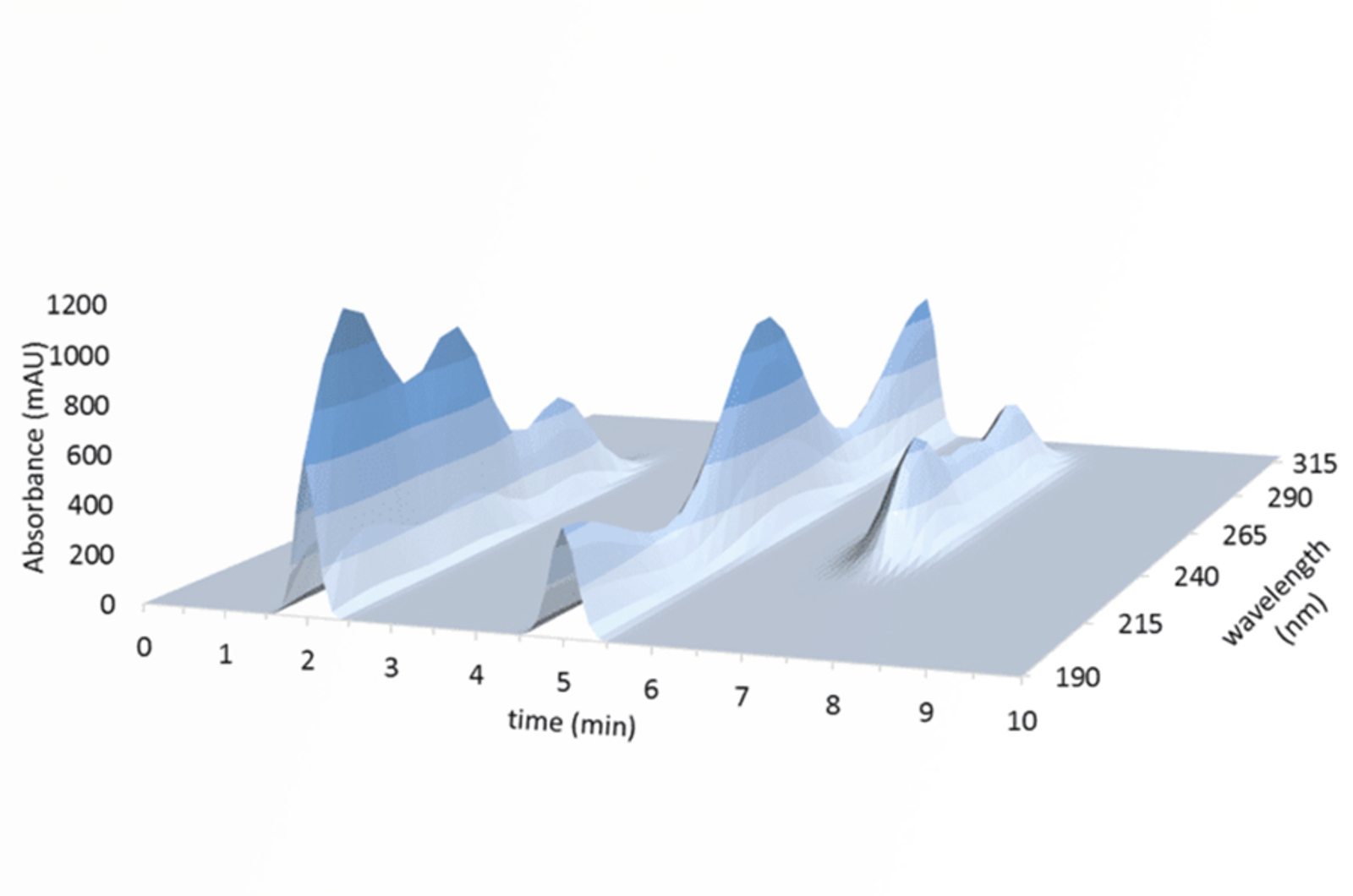
Peak Purity Algorithms Using Diode Array Detectors
In an ideal chromatographic separation, all sample components would be isolated from each other and detected as fully resolved peaks. However, it is not uncommon to encounter situations when separation is less than ideal, resulting in some degree of overlap. In extreme cases, what appears to be a single peak contains in fact two or more coeluting components. Checking the purity of such peaks is critical in order to correctly interpret the results of the analysis, which is the focus of this guide.
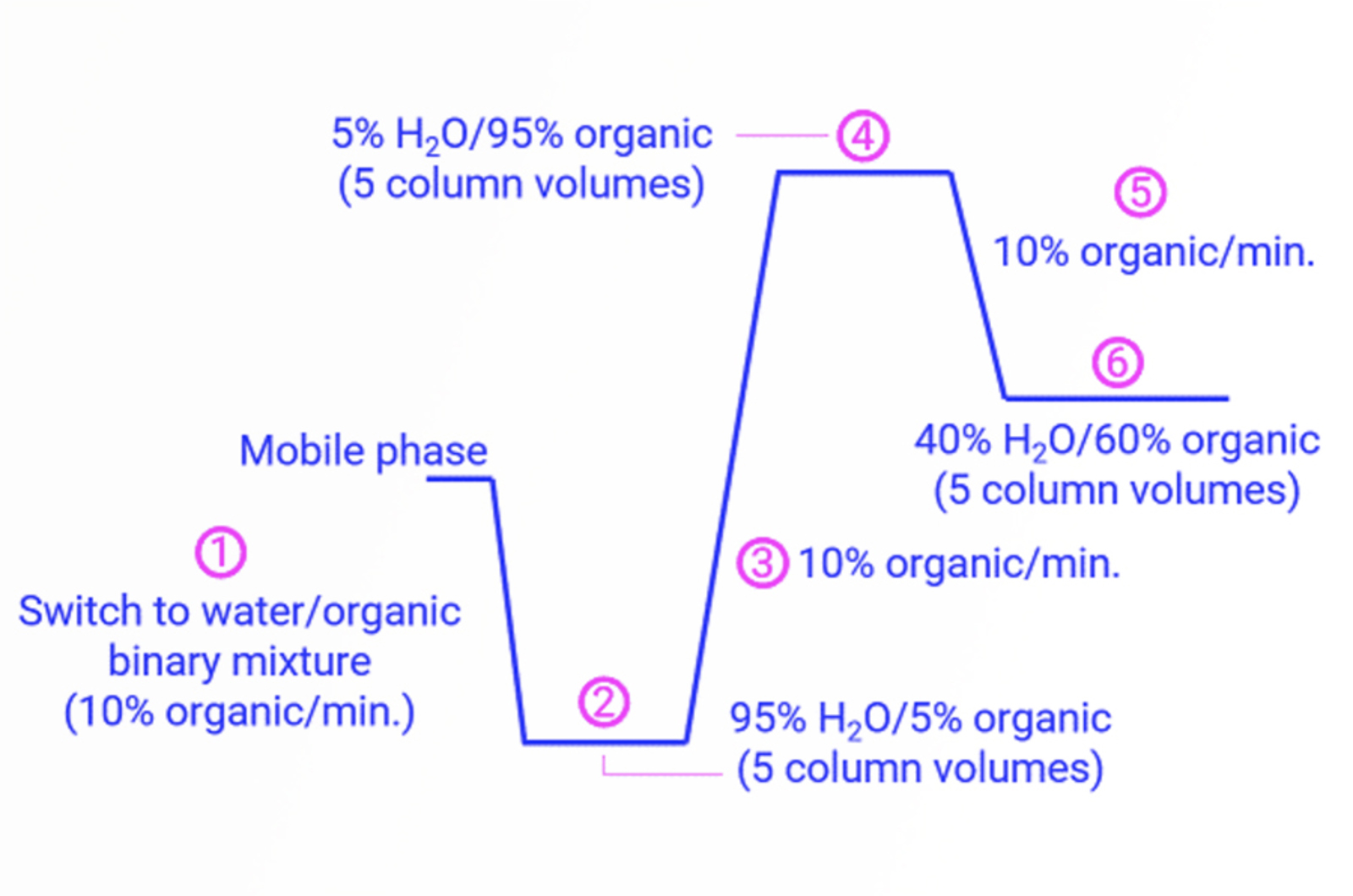
Essential HPLC Protocols
Here are some essential protocols for looking after your HPLC system and column.
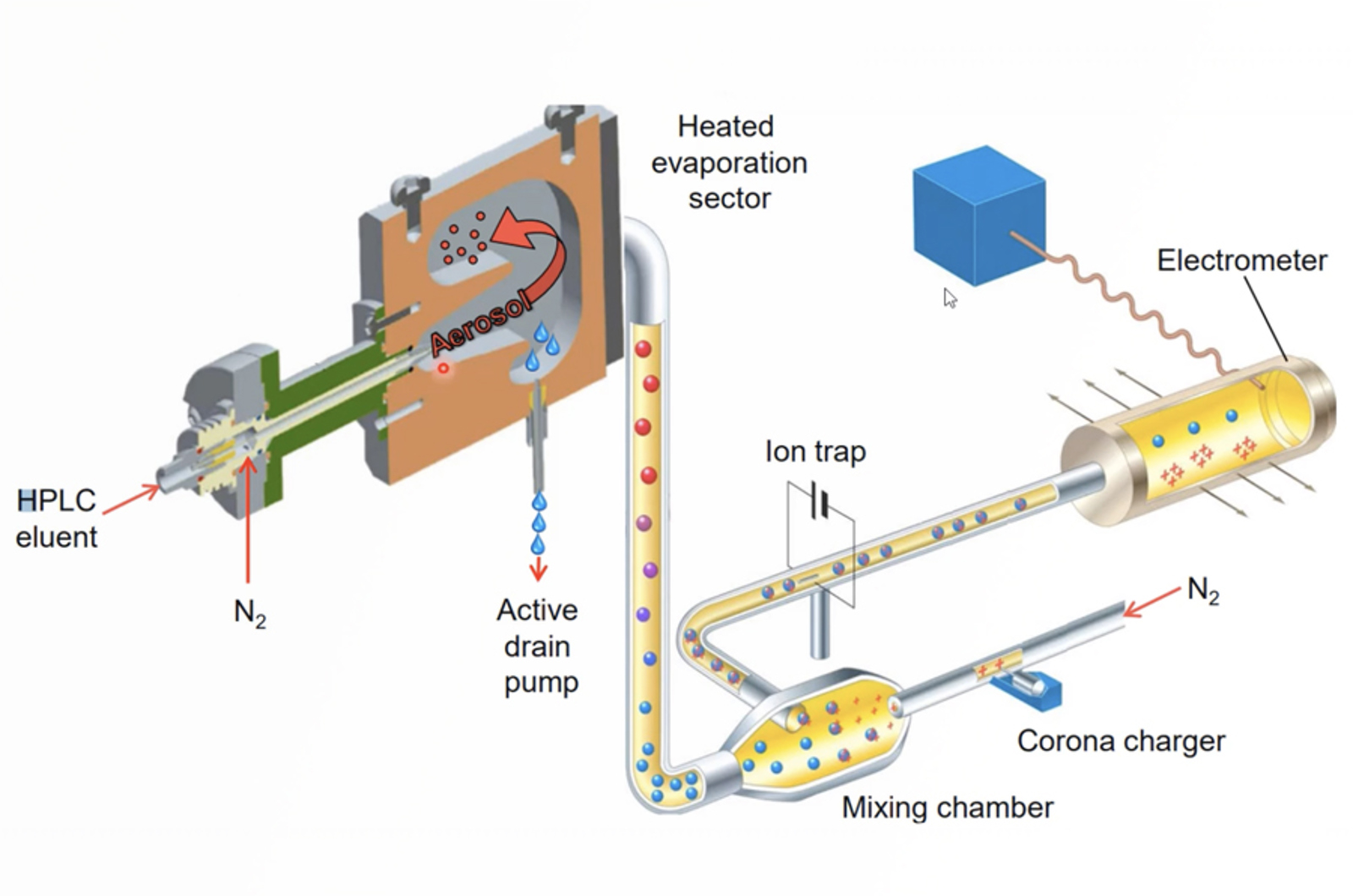
CHROMtalks - Leveraging Optimal Performance of Charged Aerosol Detection Through Optimization and Troubleshooting Techniques
In this talk, we will highlight some of the ways that CAD in particular is different from UV-absorbance detection, including non-linear response to analyte concentration, and sensitivity to mobile-phase impurities. We will show how careful optimization of parameters and troubleshooting can lead to successful development of analytical methods, nearly on par with that or conventional UV absorbance detector.
Introduction to HPLC Detectors
This module will introduce the general terms and concepts that are applicable to all HPLC detectors; including selectivity, sensitivity, limit of detection and limit of quantification. The learning content will allow you to understand the function of an HPLC detector and what is required when selecting a detector for specific analytical outcomes.
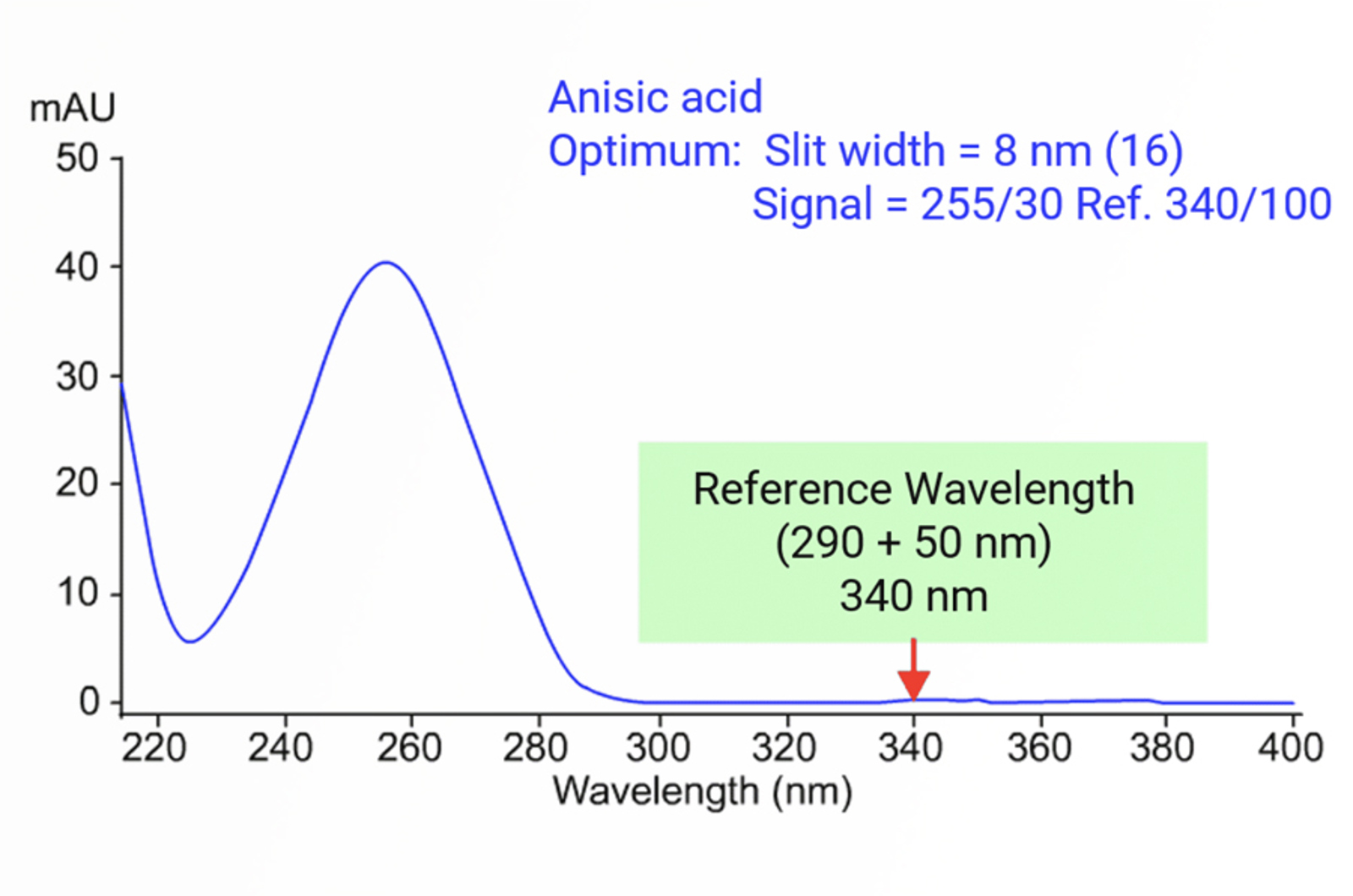
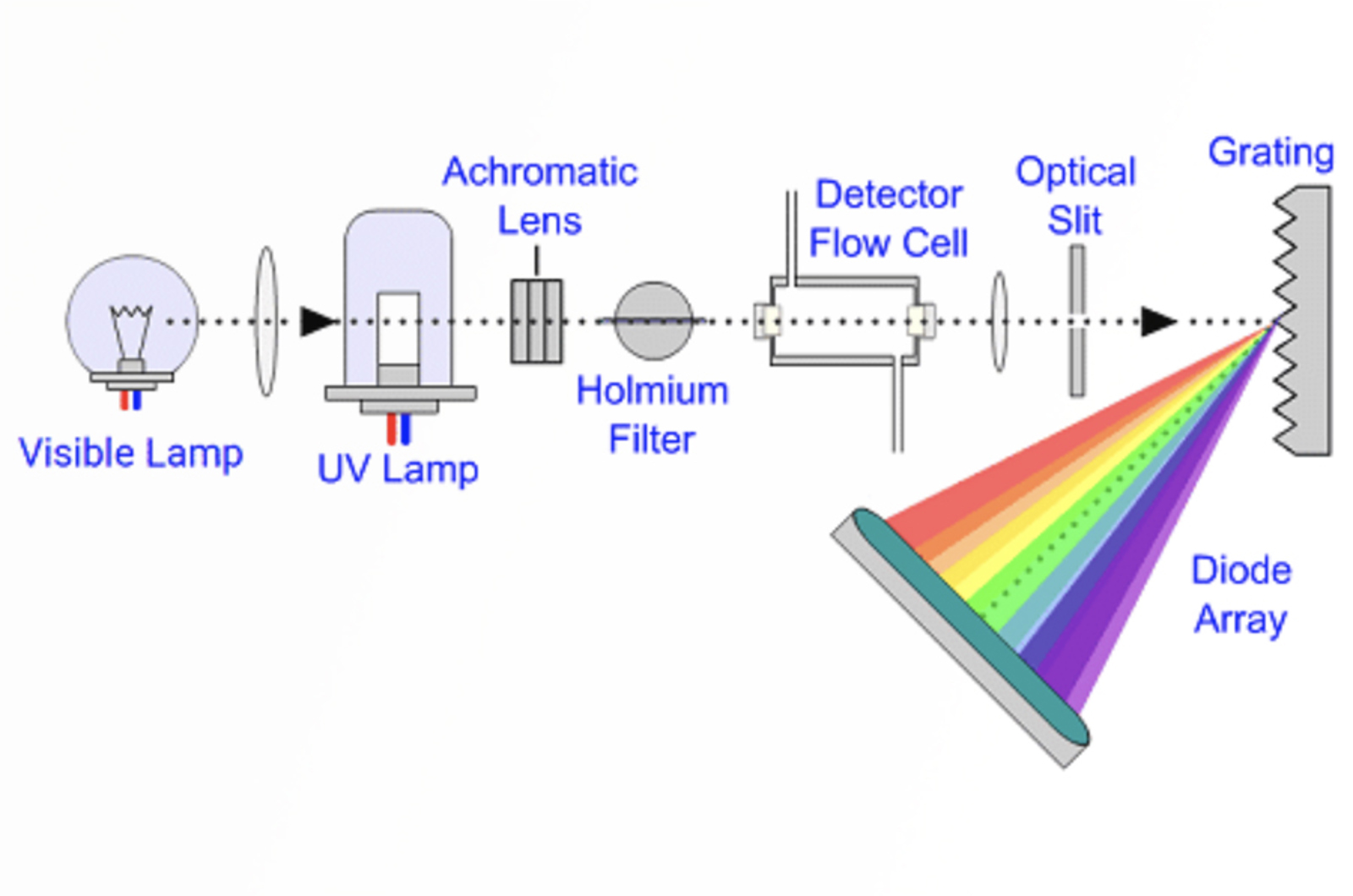
UV-Visible Detectors
The most commonly used detector for HPLC analysis is the UV-visible detector. The detector fulfills many of the criteria for an ideal detector. This module will detail the workings of UV-visible detectors, including variable wavelength and diode array detectors. Key detectors settings that should be optimized are fully detailed.

Practical HPLC Video Maintenance
This practical user maintenance module covers common HPLC maintenance operations. The video content demonstrated in this module will allow you to better care for and set up your instruments, which ensures they function correctly and produce the best possible data.
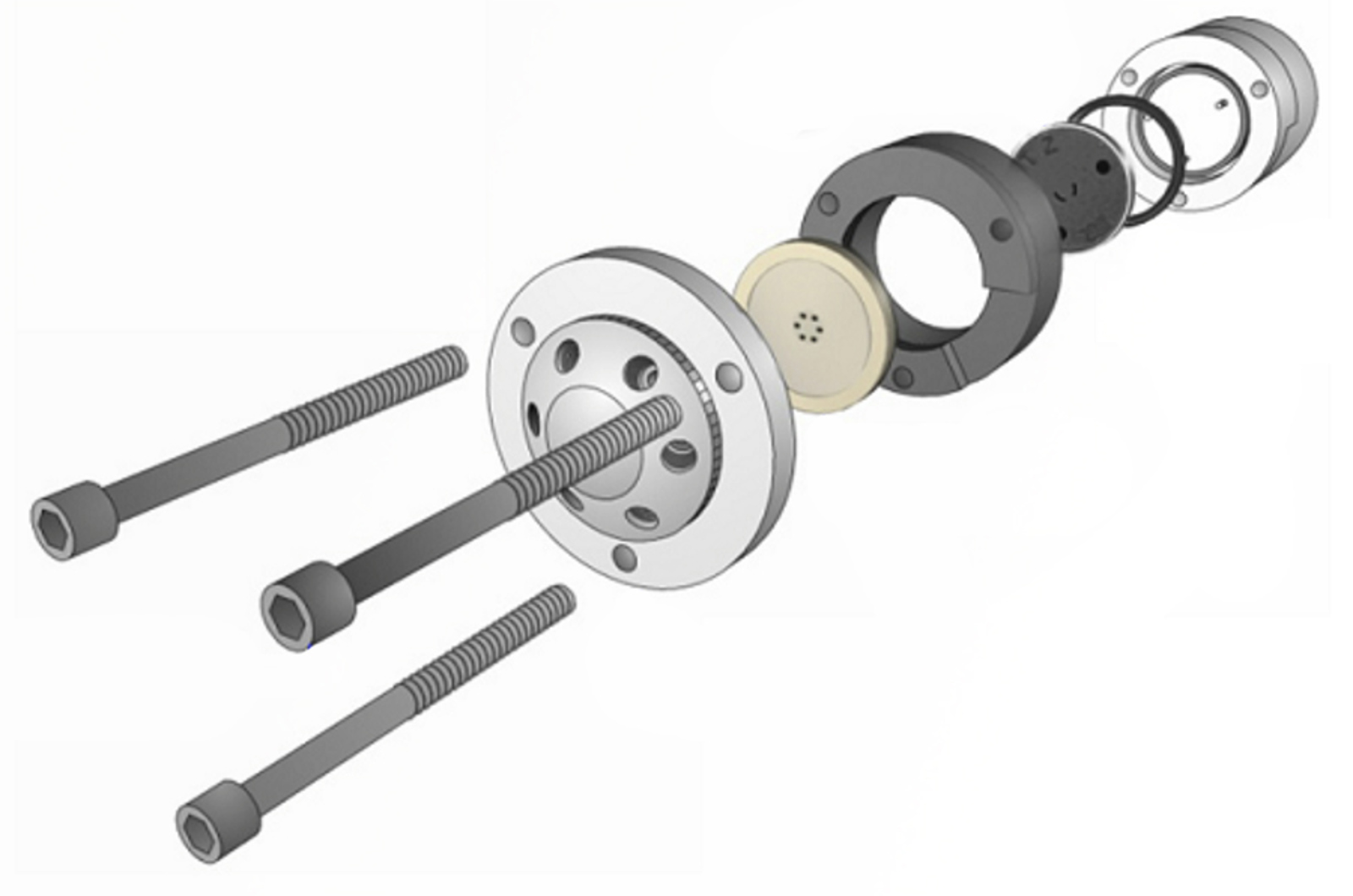

What HPLC Operators Need to Know Part 1: Everything Needed to Understand Mobile Phase Pumping Systems
This webcast discusses how and why mobile phases are chosen and prepared and the different variations of HPLC pumps and autosamplers which are available. As well as considering the role and function of the (U)HPLC pump, the differences and benefits of isocratic, binary, and quaternary pumps, the important major and minor operating variables, and how modern HPLC and UHPLC autosamplers function.
